How To Be Proactive About Concussions In Student Athletes
December 5, 2023
Most people have seen the headlines about concussions as a common sports injury—and it's natural that parents of athletes may have concerns. A large misconception in sports is that previous concussions are to be blamed for ongoing headaches, blurred vision and memory loss, among other symptoms.
 “It’s really important to think about concussions in tandem with overall brain health,” says Jake Carpenter-Thompson, M.D., Ph.D., a board-certified neurologist at the Henry Ford Kutcher Clinic for Concussion and Sports Neurology. “Concussions can be concerning, but they shouldn’t be looked at in a vacuum. It is important to understand an athlete’s overall brain health to help manage recovery after any impact.”
“It’s really important to think about concussions in tandem with overall brain health,” says Jake Carpenter-Thompson, M.D., Ph.D., a board-certified neurologist at the Henry Ford Kutcher Clinic for Concussion and Sports Neurology. “Concussions can be concerning, but they shouldn’t be looked at in a vacuum. It is important to understand an athlete’s overall brain health to help manage recovery after any impact.”
One way to do that is to consult with your child’s doctor or a sports neurologist for an annual evaluation. A sports neurologist focuses on managing sports-related brain and nervous system injuries and conditions in athletes, such as concussions, post-concussion syndrome, peripheral nerve injuries, migraines, epilepsy and more.
“Having an annual evaluation of your athlete’s brain health when they are at their baseline – and uninjured – can help diagnose and treat issues when they arise,” says Dr. Carpenter-Thompson.
A qualified healthcare professional can use the baseline evaluation results as an important comparison tool if an athlete develops a suspected concussion.
Best Practices For Keeping Athletes Safe
Dr. Carpenter-Thompson shares these tips to ensure you keep front of mind your child’s brain health and safety, not just their athletic performance:
- Get a brain health baseline test. This should include a personal and family neurological history, with a focus on current issues. It is important to note any neurological conditions that may influence concussion recovery, such as ADHD, depression, anxiety or migraine headaches.
- Encourage your children to listen to their body. There are risks to playing any sport. Encourage your child to listen to and be honest about how they’re feeling. It’s the best way to prevent and treat injuries.
- In the event of an injury, look for the signs. Within 24 hours after an injury, an athlete should be evaluated if they are experiencing: headaches, fatigue, dizziness and nausea, changes in sleep habits, trouble with memory, confusion, irritability and anxiety, or light sensitivity.
- Know that brain injuries don’t just occur with a blow to the head. They can also occur from falls, car accidents or even whiplash. If your child is experiencing any symptoms, consult your physician.
- Remember that brain health is more than just concussions. If your athlete is complaining of chronic headaches, migraines, dizziness, memory or mood issues, there may be an underlying issue.
“There is no magic number of concussions a brain can sustain. Each person is different,” says Dr. Carpenter-Thompson. “The severity of the impact and recovery time can vary greatly for numerous reasons. By getting a brain health assessment before the injury, we can provide more targeted care to improve an athlete's overall clinical course.”
To find a sports medicine doctor or athletic trainer at Henry Ford, visit henryford.com/athletes.
Coaches Guide to Nutrition: What are Macros?
April 30, 2024
Planning your meals and snacks shouldn’t be challenging.
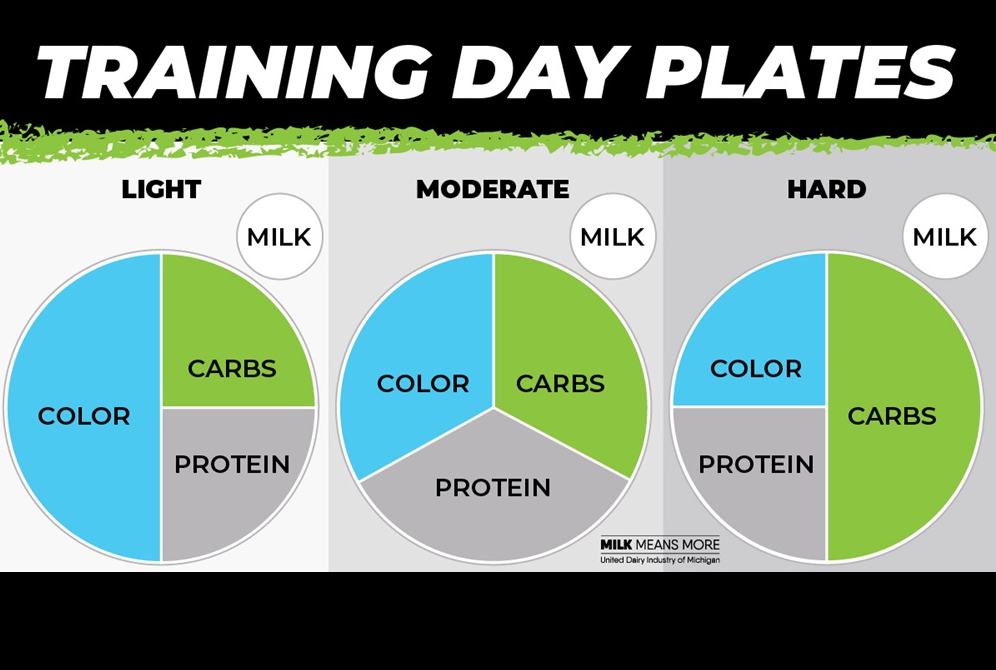
Break foods down into three categories: Carbs (energy), Protein (build and repair muscles), and Color (vitamins, minerals).
Adjust your plate based on your level of activity that day. Remember that your body needs carbohydrates like grains, fruits and vegetables for muscle fuel.
On hard training days, up to half of your plate should be carbs. On a recovery or rest day, make a quarter of your plate carbs.
Plan your meal
Check out these examples for your day’s main meals:
- Overnight oats with fruit
- Egg wrap with spinach, cheese and salsa
- Cereal with fruit and milk topped with nuts
- Smoothie made with milk, fruit, spinach and oats
- Don’t forget about school breakfast!
Lunch
- Turkey roll-up with cheese, tomato and lettuce, fruit and milk
- Grilled cheese sandwich, tomato soup, small salad, milk and pear
- Large salad with your choice of berries, grilled chicken, cheese and vinaigrette dressing, garlic bread and milk
- School lunches are made with student nutrition in mind!
Dinner
- Pasta with chicken, pesto, tomatoes and peas with milk
- Shrimp or tofu fajita bowl with brown rice, peppers, onions and shredded cheese. Add guacamole and plain Greek yogurt instead of sour cream.
- Cheeseburger made with 90 percent lean beef or turkey on a whole grain bun with lettuce and tomato and a glass of milk. Add baked sweet potato fries on the side.
Information above is excerpted from UDIM’s A Coach’s Guide to Nutrition.


