
Staying Ahead on Head Safety
July 6, 2015
By Rob Kaminski
MHSAA benchmarks editor
Three stacks of concussion-related material offered precious little space on MHSAA Executive Director Jack Roberts’ desk, and perhaps consumed even more room in his head as he tried to wrap his mind around the seemingly daily “latest and greatest” documents outlining signs, detection and return-to-play elements involving head trauma.
Without a doubt, the scene is quite similar on any given day in the offices of his cohorts across the country as school sports leaders are faced with the daunting, dizzying task of devising plans to address concerns aimed at the health of their games.
Lawmakers, rules makers, medical experts and the court of public opinion all want the same thing for student-athletes: a reduction in the chances of head-related injuries. And they all are perfectly willing to offer instant fixes to those in charge.
They often expect those in Roberts’ position to analyze, digest and create action plans as soon as possible without considering the research and resources it will take to get there.
“All parties involved want the same thing. We all want to provide the safest environment for educational athletics through protocols and practices that will offer the most minimal risk of injury,” Roberts said. “But, this can’t be accomplished through unfunded mandates which would stifle the already struggling athletic budgets in many schools.
“Changes have to occur through training and education, orchestrated through state offices and executed locally. And, it takes time to research the best and most effective means. There is so much information, and so many devices in the field today that those in athletic leadership roles almost have to have a medical background as well.”
For instance, there are documents which list as few as five symptoms for concussions, and those listing as many as 15. There are sideline detection methods which purport to take 20 minutes and those which claim to determine concussions in 20 seconds. There are as many return-to-play protocols as there are state associations.
Increasingly, state high school associations are seeking opinions and expertise from local medical personnel. In March, in one of many such meetings, Roberts and other MHSAA staff welcomed several from the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services to their office to discuss sideline detection methods and return-to-play issues.
“There are two areas that concerned us most,” Roberts said. “One, sideline detection of head injuries is inconsistent across the state in terms of both results and resources. Two, we need methods which generate immediate reports and permanent records.”
As the group which convened in March discussed the topic, potential hurdles and new perspectives on sideline management came to the forefront.
On the money and manpower front, who would be responsible for administering sideline tools? Most ideally they would need to be overseen by medical personnel rather than coaches or team managers.
From a perspective standpoint, an interesting view was volleyed out to the group: could sideline detection actually speed up a student’s return to play rather than slow it down? Current protocol prescribes that if competition continues while an athlete is withheld for an apparent concussion, that athlete may not be returned to competition that day but is subject to the return-to-play protocol. And, clearance may not be on the same date on which the athlete was removed from play. Only an M.D., D.O., Physician’s Assistant or Nurse Practitioner may clear the individual to return to activity. With immediate sideline detection, are parties more vulnerable should a student pass immediate tests, only to have undetected effects of the incident increase over time?
“The group shed a different light on the various scenarios, which was a primary purpose for the meeting,” Roberts said. “As one can see, there are so many variables to consider when attempting to determine the next plausible and practical steps toward minimizing and detecting head injuries.
“Further, we have to take into consideration practice sessions as well as competitions, and all sports, not just select sports.”
Adding to the challenge is simply the nature of athletics. Competitors at any level are just that: competitive. Often, students – or their parents – will attempt to hide symptoms or be reluctant to come forward with injuries, particularly head injuries which can’t be seen.
In more cases, perhaps the symptoms simply are not recognized, which is why education is paramount.
First, association leaders have to tackle the due diligence of researching issues and potential solutions to situations currently threatening the well-being of scholastic sports. Considering that some 1,620,000 results are offered when “sideline concussion detection tools” is typed into a search engine, this is a laborious and continual chore.
Such information then needs to be packaged and presented to leaders at the local levels – athletic directors – to pass on to coaches, the individuals who have as much or more influence on students that perhaps any other adults, including parents in some cases.
This is why MHSAA rules meetings, Coaches Advancement Program sessions and other statewide forums continue to bang the drum on health and safety issues; to make sure the messages and procedures reach the student-athletes.
And, it’s why the MHSAA is asking coaches and ADs to be accountable in verifying that the plans in place are being carried out.
Less Could Mean Less
There are times when it’s good to say, “less means more,” but in the case of contact sports, practices and competitions, the idea is for less to mean less. As in less time for collisions to occur yielding fewer injures.
It’s early yet, and one year does not constitute a large sample size, but the MHSAA Football Practice Policy instituted last August could be one step toward reducing head injuries.
Beginning this past football season, the number of practices with helmets, shoulder pads and full pads were limited to start the season, and preseason “collision” sessions were limited to one per day. During the season, such practices were limited to two per week, while the length of practices was also regulated.
Dr. Steven Broglio of the University of Michigan Neurosport department is conducting a three-year study of the Ann Arbor Gabriel Richard football program with the assistance of Richelle Williams to determine the “Effects of Concussion and Sub-Concussion.” The study began in 2013, one year prior to the new MHSAA guidelines.
Research in 2013 showed approximately 650 “impacts” per player. In 2014, the number dropped to approximately 500 impacts per player. Impacts are defined as greater than 10 gs of acceleration. Williams stated that a slap on the back is 4 g, coughing is 3.5 g. On average, a helmet hit is 25-45 g. Concussions usually happen (roughly) between 80-150g.
An encoder is embedded into each football athlete’s helmet which monitors head impacts and exactly where the impact is located. Williams sits at each practice and game and through a pager identifies the player’s number and impact from a hit of 90g or more.
They are also looking at those who do not sustain an impact concussion, but rather sustain multiple head impacts and whether those multiple head impacts lead up to brain changes (measured through EEG).
The initial findings, as submitted by the study team, indicated two reasons why there were fewer overall impacts from 2013 to 2014:
Primary reason: The MHSAA adoption that became effective in August 2014 with new limitations that were placed on “collision practices” and conditions that full pads could not be worn until the fifth day of team practice.
Secondary reason: Fewer players evaluated in 2014 than 2013.
Fit for a King?
Editor’s Note: There are many sideline detection tools on the market, as a quick Google on the topic will reveal. The following, the King-Devick test, is among the highly recommended tests, summarized here simply to provide an idea of the types of systems available and how they operate. The following is from King-Devick’s website.
The King-Devick Test is an objective remove-from-play sideline concussion screening test that can be administered by parents and coaches in minutes. The King-Devick Test is an accurate and reliable method for identifying athletes with head trauma and has particular relevance to: Football, Hockey, Soccer, Basketball, Lacrosse, Rugby, Baseball, Softball and Other Collision Activities.
King-Devick Test is an easy-to-administer test which is given on the sidelines of sporting events to aid in the detection of concussions in athletes. King-Devick Test (K-D Test) can help to objectively determine whether players should be removed from games. As a result, King-Devick Test can help prevent the serious consequences of repetitive concussions resulting from an athlete returning to play after a head injury.
How King-Devick Test Works
Concussions are a complex type of brain injury that is not visible on routine scans of the brain, yet are detectable when important aspects of brain function are measured. King-Devick Test (K-D Test) is a two-minute test that requires an athlete to read single digit numbers displayed on cards or on an iPad. After suspected head trauma, the athlete is given the test and if the time needed to complete the test is any longer than the athlete’s baseline test time, the athlete should be removed from play and should be evaluated by a licensed professional.
Remove-From-Play vs. Return-To-Play
Both remove-from-play and return-to-play decisions are crucial in concussion recovery. It is critical to remove a concussed athlete from play in order to prevent further damage. It is also extremely important to keep the athlete from returning to play until they have made a full recovery. There are tools to assist in making both remove-from-play and return-to-play decisions.
King-Devick Test for Remove-From-Play Decisions
- Quick, objective sideline testing
- Measures impairments of speech, language and other correlates of suboptimal brain function
- Instant screening feedback in minutes
- Administered by parents, coaches, athletic trainers and medical professionals in remove-from-play decisions
- Neurocognitive Testing for Return-To-Play Decisions
- Computerized concussion evaluation system (in the computer lab)
- Measures verbal and visual memory, processing speed and reaction
- Tracks recovery of cognitive processes following concussion
- Assists clinicians in making return-to-play decisions
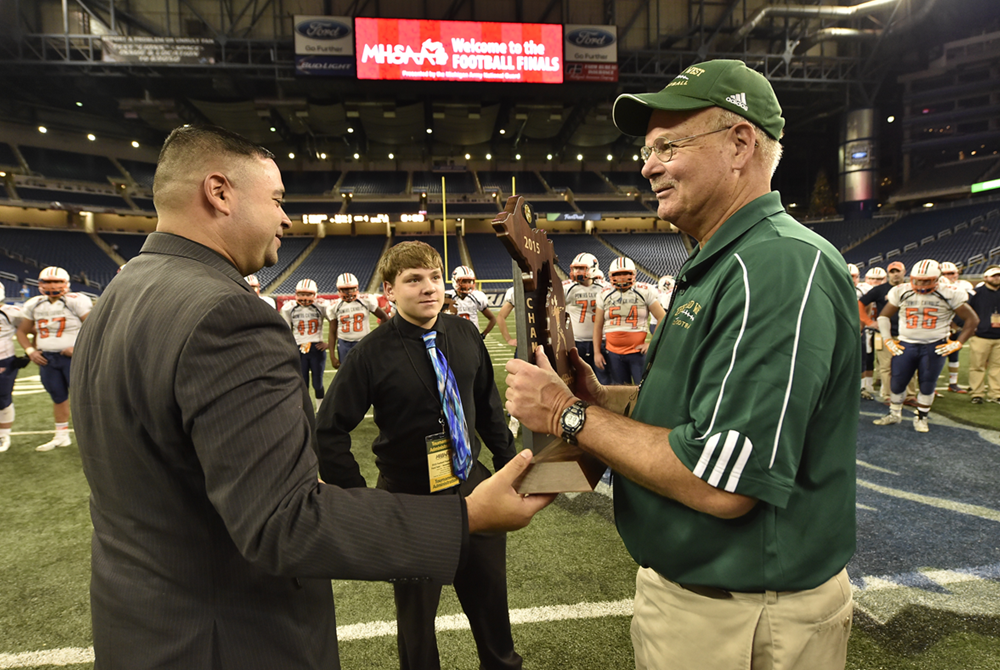

Process, Relationships Still Matter Most as 4-Time Champ Shillito Coaches 41st Season
By
Steve Vedder
Special for MHSAA.com
October 18, 2024
It was John Shillito's third year as Muskegon Orchard View football coach, and while the wolves weren't exactly knocking at the door, some faint low growls could clearly be heard.
Shillito had been successful at Comstock Park with his teams going 21-8 over three seasons, but the move to Orchard View included 3-6 and 4-5 records the first two.
While there wasn't yet widespread anxiety, Shillito recalls there was a bit of concern.
"I was much younger then and wasn't as successful yet in education," Shillito said. "But we weathered it and came through the other side. But you wonder a little; there's always a little self-doubt. I think it was important to go through it, because you can learn as much even when you're not winning."
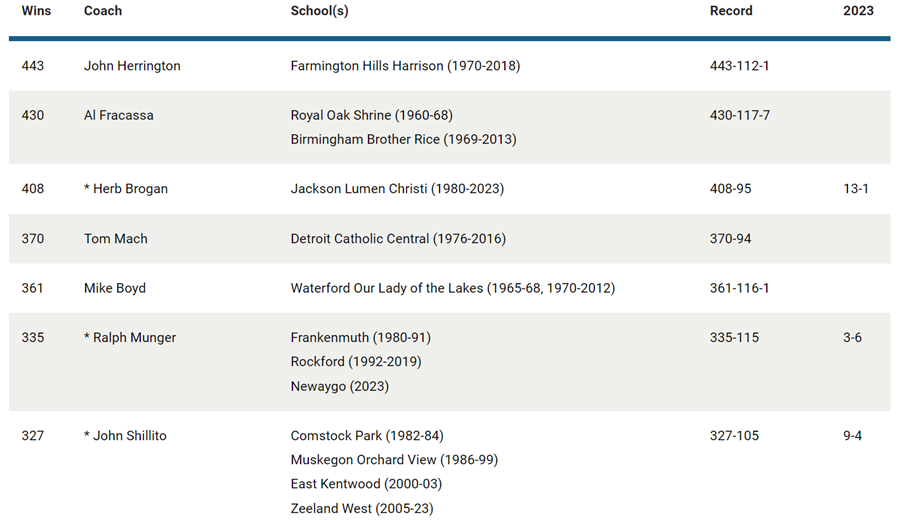
Michigan high school football is the better for Shillito sticking it out. Two schools later, Shillito finds himself as the state's third winningest active coach and seventh overall with a 333-106 mark over 41 seasons.
His Zeeland West team is 6-1 this season and likely to become his 27th team – and 15th in a row – to qualify for the playoffs. Shillito's teams at Byron Center, Muskegon Orchard View, East Kentwood and Zeeland West have won a combined 16 conference titles.
Not bad for someone whose first love was baseball. Shillito's father, Harry, played three seasons professionally in the Brooklyn Dodgers system during the "Boys of Summer" era of the 1940s and 50s. Shillito grew up as a talented catcher in the spring and top football prospect as a defensive lineman in football. When programs such as Central Michigan, Eastern Michigan and Northern Michigan began showing an interest, the lure of a football scholarship made it an easy decision which sport he would follow.
After playing three years at Central Michigan, his coaching career kicked off with an assistant gig at Central Bucks East in Pennsylvania in 1980. He became head coach at Comstock Park in 1982.
 Shillito said the same motivation which drove him into coaching has kept him in the sport for nearly five decades. It's not necessarily winning state championships – he’s won four at Zeeland West – or fulfilling a deep competitive drive or even the lure of Friday Night Lights in a small community. It's showing up at practices, adhering to a process and building and honing relationships with players and other coaches.
Shillito said the same motivation which drove him into coaching has kept him in the sport for nearly five decades. It's not necessarily winning state championships – he’s won four at Zeeland West – or fulfilling a deep competitive drive or even the lure of Friday Night Lights in a small community. It's showing up at practices, adhering to a process and building and honing relationships with players and other coaches.
Take those away and the 67-year-old Shillito, a member of the Michigan High School Football Coaches Association Hall of Fame, would definitely be looking elsewhere to spend Friday nights in the fall.
"It's the process; I love a good practice. You know when (it's good) and when it isn't. More than even the football, it's the coaching process and the people I work with," he said.
"Winning is a week-to-week deal. This week's game is what we're all about. And then in the offseason, it's preparation for the year coming up. The state titles are always a bonus."
Which isn't to say Shillito isn't competitive. Whether it’s been playing hockey, wiffle ball, 3-on-3 basketball or backyard football with his brothers, Shillito's competitive spirit has thrived.
"Oh yeah," he said. "But I'm a glass half full-type competitor. I can find the positive side in either wins or losses. But for me it's about the preparation, no doubt about it."
Shillito's success has come even with opponents knowing exactly what they'll see offensively from his teams: the famed wing-T offense, which he's run since the mid-1990s and was taught to him by famed West Michigan coach Irv Sigler. In fact, Shillito said if there is anything responsible for his success, it's the ability to implement what he's learned from coaches as a whole such as Mike Henry, the longtime basketball coach at Orchard View, or former Remus Chippewa Hills football coach Ron Reardon.
When he first got into coaching, Shillito said the wing-T seemed the easiest to teach. He's tweaked the process over the years, but it's been highly successful for him wherever he's coached. The number of Michigan teams which run the wing-T has probably lessened over the years as passing has taken over many high school offenses. But Shillito said the run-first philosophy can still be found in pockets all over the state. Shillito said he has no second thoughts about devoting his offense to the wing-T, and the success only underscores the point.
"It can be difficult if you're not winning, no doubt about it," said Shillito, who figures he's coached about three dozen 1,000-yard rushers. "But the value in the system is that it's an easier process. That is, if you get a buy-in from the players and community. We've had that at Zeeland West."
 As the sun begins to set on Shillito's coaching career, he's hard-pressed to pick his best, favorite or most surprising teams. For starters, there's the 1983 Byron Center team which reached the Class C Semifinals, or the 1995 and 1999 Orchard View teams which played in Class B Finals and combined for a 24-3 mark.
As the sun begins to set on Shillito's coaching career, he's hard-pressed to pick his best, favorite or most surprising teams. For starters, there's the 1983 Byron Center team which reached the Class C Semifinals, or the 1995 and 1999 Orchard View teams which played in Class B Finals and combined for a 24-3 mark.
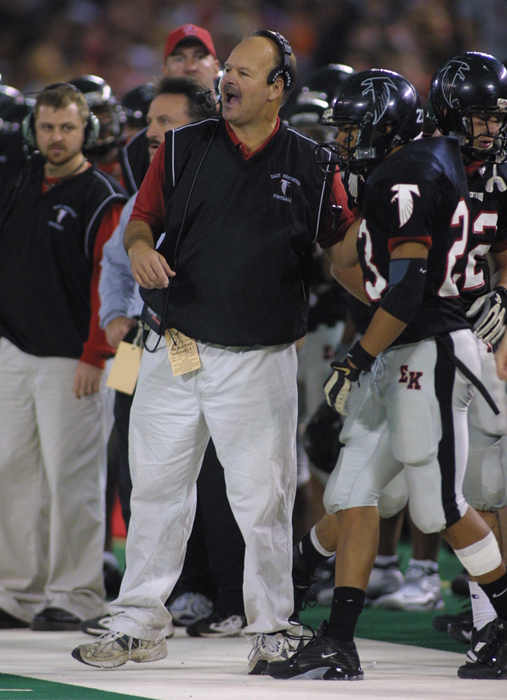
Or maybe the 13-1 Division 1 runner-up club at East Kentwood in 2002, and the 2006 Zeeland West team which claimed the Division 4 title after winning its last 11 games by an average of 35 points per. Or the 2011 Zeeland West team which went 14-0 to kick off a phenomenal five-year stretch during which the Dux went a combined 60-6.
Ask Shillito about any of those seasons, and his answer as to what he remembers most about his coaching career may be surprising. Many of his most cherished moments include his teams going just 5-6 over the years against Muskegon, including three playoff losses that ended the Dux's season. Balance that with his record against other programs, such as a 73-16 mark against other Lakeshore teams, including an 18-7 record against rival Zeeland East. Or a 10-4 record against traditional Grand Rapids-area powers such as Lowell, Grand Rapids Catholic Central, South Christian, West Catholic and Hudsonville. In the postseason, Shillito's teams are an amazing 54-22 over 26 seasons in the MHSAA Playoffs.
As for knocking heads with Muskegon, Shillito said the thrill of a great rivalry and the consistency his teams have shown over the years is what has always driven him.
"It's the longevity and consistency," Shillito said. "I've gotten to work with great people who have had an equal share in this. I've had such a wide variety of guys I've worked with in four programs, and it’s meaningful. "
He is coy on when he might finally call it a career. He could wake up tomorrow and decide it's the time, or it could be next week, the end of the season or maybe one more season. Who's to say?
"We're getting close now," he will say. "We're always in the moment; that's just where we are. Then we'll evaluate things after the season. That's been true now for several seasons."
PHOTOS (Top) Zeeland West football coach John Shillito, right, receives the Division 4 championship trophy from MHSAA Representative Council member Orlando Medina in 2015 at Ford Field. (Middle) Entering this season, Shillito ranked seventh all-time and third among active coaches for football victories in the MHSAA record book. (Below) Shillito prepares to send in one of his East Kentwood players during the 2002 Division 1 Final at Pontiac Silverdome. (MHSAA file photos.)

