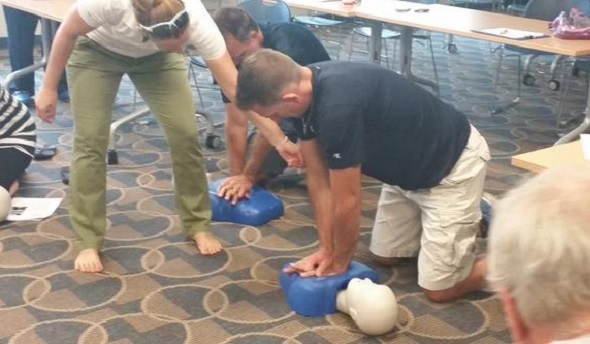
CPR Training, CAP Add to Preparedness
By
Geoff Kimmerly
MHSAA.com senior editor
October 12, 2015
A recent graduate from Ovid-Elsie High School named Chris Fowler started classes this fall at Michigan State University, his days representing the Marauders on the basketball court, football field and golf course now memories as he starts the next chapter of his young adult life.
But his story also will remain a reminder as his high school’s athletic department prepares each year to keep its athletes as safe as possible.
Three years ago next month, Fowler collapsed on the football practice field in cardiac arrest. The then-sophomore was brought back to life by two of his coaches, who revived him with CPR and an AED machine.
There’s no need for athletic director Soni Latz to recount the events of that day when explaining the importance of being ready to respond to a medical crisis – her coaches are well aware of why Fowler survived and understand completely why they too must be prepared.
“Everyone is very aware of what happened and the importance of being trained and knowing what to do, and actually feeling comfortable to step in and administer CPR when needed,” Latz said. “You can feel it’s never going to happen to you, but once it has, it makes you more aware and conscientious to be prepared.”
But Fowler’s story is worth noting on a larger level as varsity coaches at all MHSAA member schools are required this year for the first time to become certified in CPR, and as the largest classes in Coaches Advancement Program history begin course work that includes up to four modules designed to make them aware of health and safety situations that may arise at their schools as well.
The CPR requirement is the most recent addition to an MHSAA thrust toward raising expectations for coaches’ preparedness. The first action of this effort required all assistant and subvarsity coaches at the high school level to complete the same rules and risk minimization meeting requirement as high school varsity head coaches beginning with the 2014-15 school year.
The next action, following the CPR mandate, will require all persons hired as a high school varsity head coach for the first time at an MHSAA member school after July 31, 2016, to have completed the MHSAA’s Coaches Advancement Program Level 1 or Level 2.
In addition, MHSAA member schools this summer received the “Anyone can Save a Life” program, an emergency action plan curriculum designed by the Minnesota State High School League to help teams – guided by their coaches – create procedures for working together during medical emergencies.
“Coaches get asked to do a lot, and even if a school has an athletic trainer or some other health care professional, that person can’t be everywhere all the time. Coaches often are called upon to be prepared for (medical) situations,” said Gayle Thompson, an adjunct assistant professor at Albion College who formerly directed the athletic training program at Western Michigan University and continues to teach CAP sports medicine modules.
“The more (coaches) can learn to handle the situations that can inevitably arise, the better off they’re going to feel in those situations and the better care they’ll be able to offer their athletes. It’s proven that the faster athletes are able to get care, the quicker they’re able to come back to play.”
 Pontiac Notre Dame Prep – which has sent a number of coaches through the CAP program – began a focus on heart safety about five years ago after a student-athlete was diagnosed with a heart issue that allowed her to continue to play volleyball and softball, but not basketball. Athletic director Betty Wroubel said that prior to the student’s diagnosis, the school did provide training in CPR, AED use and artificial respiration; however, that situation put coaches and administrators further on the alert.
Pontiac Notre Dame Prep – which has sent a number of coaches through the CAP program – began a focus on heart safety about five years ago after a student-athlete was diagnosed with a heart issue that allowed her to continue to play volleyball and softball, but not basketball. Athletic director Betty Wroubel said that prior to the student’s diagnosis, the school did provide training in CPR, AED use and artificial respiration; however, that situation put coaches and administrators further on the alert.
Her school offers CPR training also to subvarsity and middle school coaches, using a combination of video instruction from the American Red Cross and in-person guidance by members of the school community who are certified to teach those skills. Students at the school also have received training – and it paid off a few years ago when one of them gave CPR to a baby who had stopped breathing at a local shopping mall.
Portage Central scheduled two sessions this fall for its coaches to receive not only CPR certification, but AED training as well. Central was fortunate to have an American Red Cross first-aid trainer in house, teacher Rachel Flachs, who also is close to the athletic side as the girls swimming and diving coach at Mattawan High School.
Central athletic director Joe Wallace said the training was offered not just to varsity head coaches, but every head coach on every level of the program so that “at least we know that at every given practice, every game, we’d have someone recently trained,” he said.
And he was proud of how his coaches immersed themselves in the subject matter.
“They were putting themselves in scenarios to see how it related to their own sports and asking really great questions,” Wallace said. “It was thought provoking.”
The CAP sports medicine modules are designed to do the same as coaches consider the medical situations they could face. They aren’t designed as “medical training,” said Tony Moreno, a professor of kinesiology at Eastern Michigan University and teacher of all four CAP sports medicine modules. Rather, attendees receive an awareness and basic education on common injuries, injury mechanisms and prevention, and how to create an action plan in the event of an injury incident.
The CAP program touches on a variety of safety topics in several of the available seven levels of coach education.
CAP 1 – which is part of the mandate for new coaches beginning next school year – includes “Sports Medicine and First Aid.” Cap 4 has modules titled “Understanding Athlete Development” and “Strength and Conditioning: Designing Your Program.” CAP 5 includes the session, “Peak Health and Performance.” Attendees also have the option of receiving CPR and AED training as an addition to some courses.
With a quick Internet search, coaches have no trouble finding a variety of resources on sports medicine, performance enhancement, nutrition and healthy living regarding young athletes. “However, some of these sources are more credible and scientifically-based in comparison to others,” Moreno said. “CAP strives on an annual basis to continue to update and improve the quality and credibility of this information and in a face-to-face manner where coaches have the opportunity to ask questions about their experiences and specific programs.”
“Having the CAP requirement will only make them better informed. Many have had this kind of information before, but there’s always something new coming,” Thompson added. “I think we do a good job, not of trying to tell them they were wrong, but maybe taking what they’ve known a step further and making them better prepared – empowering them to do their best.”
Wroubel may understand more than most athletic directors the growing list of tasks coaches are asked to accomplish; she’s also one of the winningest volleyball and softball coaches in MHSAA history and continues to guide both Fighting Irish programs.
But she and Wallace both said the CPR mandate isn’t considered another box to check on a to-do list; there’s enthusiasm because of its importance and the opportunity to carry those skills into other areas of community life as well.
Wroubel has served as a coach since 1975 and said this renewed emphasis on coaches having knowledge of sports medicine actually is a return to how things were when she started. Back then, coaches were responsible for being that first line of medical know-how, from taping ankles to providing ice and evaluating when their athletes should make a trip to the doctor’s office.
“When I first started coaching, we didn’t have sports medicine people, trainers, or team doctors other than for football. You did everything yourself,” Wroubel said. “I think everybody got away from that, but I think it’s coming back because a trainer can’t be everywhere.
“It’s healthy and it’s good for kids. … The more of us with emergency skills, the better we’re able to serve our community.”
PHOTOS: (Top) Portage Central coaches receive CPR training earlier this fall. (Middle) Pontiac Notre Dame Prep coaches practice during AED training. (Photos courtesy of school athletic departments.)

Michigan Leaders in 3 Sports Earn National Honors from NFHS Coaches Association
By
Geoff Kimmerly
MHSAA.com senior editor
January 16, 2024
Detroit Cass Tech boys basketball coach Steve Hall, Farmington Hills Mercy girls golf coach Vicky Kowalski and East Grand Rapids girls swimming & diving coach Butch Briggs and have been named a 2022-23 National Coach of the Year in their respective sports by the National Federation of State High School Associations (NFHS) Coaches Association.
They were selected by a committee including representatives from all eight NFHS sections – Michigan is part of Section 4 with Illinois, Indiana, Iowa and Wisconsin.
The following brief bios include an excerpts from each honoree’s coaching philosophy, which nominees were asked to submit after being identified as candidates for the awards.
 Steve Hall guided Detroit Cass Tech to its first MHSAA Finals championship last season as the Technicians capped a 28-1 run. He’s 160-30 in his eighth season directing Cass Tech, with his team 9-0 this winter, and he has a career high school record of 370-103 having also coached at Detroit Rogers (1996-97 through 2004-05) and Detroit Northwestern (2005-06 through 2007-08). He led Rogers to three straight Class D championships from 2003-05, led Northwestern to its first Detroit Public School League championship in 30 years and Cass Tech to its first in the PSL in 19 seasons. He also coached collegiately as an assistant at Duquesne University (2008-09 through 2011-12) and Youngstown State University (2011-12 through 2014-15) before taking over at Cass Tech for the 2015-16 season. He has received multiple state Coach of the Year awards during his tenures at Rogers and Cass Tech, and also serves the latter as athletic director and boys cross country coach.
Steve Hall guided Detroit Cass Tech to its first MHSAA Finals championship last season as the Technicians capped a 28-1 run. He’s 160-30 in his eighth season directing Cass Tech, with his team 9-0 this winter, and he has a career high school record of 370-103 having also coached at Detroit Rogers (1996-97 through 2004-05) and Detroit Northwestern (2005-06 through 2007-08). He led Rogers to three straight Class D championships from 2003-05, led Northwestern to its first Detroit Public School League championship in 30 years and Cass Tech to its first in the PSL in 19 seasons. He also coached collegiately as an assistant at Duquesne University (2008-09 through 2011-12) and Youngstown State University (2011-12 through 2014-15) before taking over at Cass Tech for the 2015-16 season. He has received multiple state Coach of the Year awards during his tenures at Rogers and Cass Tech, and also serves the latter as athletic director and boys cross country coach.
“My coaching philosophy is ‘Learning Life Skills Through Basketball.’ I have encountered many youngsters that value basketball more than anything. Therefore, I use basketball as a carrot to dangle to help them acquire life skills and other necessities that can benefit them in their lives. Ultimately, when the ball stops bouncing they may be quality fathers, husbands, principals, CEOs, etc., and positive contributors to society. My motto is, “Be better today than yesterday and better tomorrow than today.” My athletic philosophy is scholarships and championships in that order! We love to win. But winning is not only on the scoreboard but also in life. Accountability, Reliability, Dependability and Responsibility. “Do what you are supposed to do, be where you are supposed to be, every play and every day.” God has blessed me with high morals, values and unmatched energy to leave my student athletes better than I found them.”
 Vicky Kowalski completed her 46th season this fall coaching Farmington Hills Mercy’s girls golf team, and led the program to its second-straight Lower Peninsula Division 2 championship and fourth MHSAA Finals title overall. Her teams also have won seven Regional and 21 league championships and were 220-50 in matches entering the season. She has received several coaching awards over the years including statewide awards from the Michigan Interscholastic Golf Coaches Association (MIGCA) and Michigan High School Coaches Association (MHSCA). Kowalski also is in her 22nd season as Mercy’s girls bowling coach and has coached multiple subvarsity seasons of basketball and volleyball as well. She’s been inducted into Halls of Fame by both MIGCA and the Michigan High School Interscholastic Bowling Coaches Association (MHSIBCA).
Vicky Kowalski completed her 46th season this fall coaching Farmington Hills Mercy’s girls golf team, and led the program to its second-straight Lower Peninsula Division 2 championship and fourth MHSAA Finals title overall. Her teams also have won seven Regional and 21 league championships and were 220-50 in matches entering the season. She has received several coaching awards over the years including statewide awards from the Michigan Interscholastic Golf Coaches Association (MIGCA) and Michigan High School Coaches Association (MHSCA). Kowalski also is in her 22nd season as Mercy’s girls bowling coach and has coached multiple subvarsity seasons of basketball and volleyball as well. She’s been inducted into Halls of Fame by both MIGCA and the Michigan High School Interscholastic Bowling Coaches Association (MHSIBCA).
“I have always believed in participation. On all the teams I have coached, everyone plays – no one sits the bench. All my athletes have their opportunities to grow in the sport. I have always preached dedication and sportsmanship. The athletes practice well to perform well. They encourage teammates as well as competitors. I enjoy interaction with other coaches. We share coaching techniques and ideas for improving team performance.”
Milton “Butch” Briggs has led the East Grand Rapids girls swimming & diving team to a record 26 MHSAA Finals team championships, the first in 1978 and including six straight from 1981-86 and the program’s current three-year title streak. His girls program also has celebrated 105 individual or relay Finals champions and clinched 33 league team titles. Briggs has received several coaching awards, including nationally for his sport (girls and boys combined) from the National High School Athletic Coaches Association (NHSACA) in 2000 and the NFHS Coaches Association for boys swimming & diving in 2011. He entered this past fall season with a dual meet record of 522-65-1 over his career, which has spanned 49 years total, and his boys teams have won 12 MHSAA Finals. Briggs also has served as an assistant track coach at multiple schools and as MISCA president, and is in the MHSCA Hall of Fame.
“My coaching philosophy has been, and continues to be, a work in progress. I have formed relationships with hundreds of amazing young people. They have taught me life lessons in real time and real situations. As a neophyte coach, the experience revolved around winning. We worked together as a team, supported each other in and out of the pool, and won often. Thankfully, I became aware of the value within each athlete. Today, I attempt to interact with each athlete at every team activity and follow their progress in non-swimming endeavors. In short, when I removed my ego from the team's expectations and outcomes, the entire atmosphere was much more enjoyable and productive. And we are still capable of being successful. The Lord has put me in the right place at the right time.”
Six more Michigan coaches earned honors in Section 4. Stefanie Kerska was honored in boys swimming & diving after leading Ann Arbor Pioneer to its third-straight Lower Peninsula Division 1 Finals title under her leadership, and Asa Kelly was recognized in boys track & field after leading Benzie Central to the LPD3 Finals championship. Mt. Morris volleyball coach James Pender was honored after leading his team to the Division 2 Quarterfinals in 2022, when he also eclipsed 1,000 career coaching wins in the sport, and Traverse City St. Francis’ Julie Duffing was awarded in cross country after leading her program to the 2022 LPD3 Finals championship, the program’s second under her leadership. Haslett/Williamston girls lacrosse coach Chad Pastor was honored after leading his team to the Division 2 Semifinals last spring, and Hartland competitive cheer coach Candace Fahr was recognized after leading her team to the MHSAA Finals for the fourth time in her six seasons guiding the program.
The NFHS has been recognizing coaches through an awards program since 1982.

