
50 Years Later, 'Charlie' Remains Legendary
By
Ron Pesch
MHSAA historian
September 30, 2018
By Ron Pesch
Special for Second Half
There is no official record of the proceedings, only a short newspaper recap of the event that was hosted 50 years ago at Michigan State’s Kellogg Center. In attendance was a who’s who of high school sports administrators. They were there to honor the man, affectionately known to his friends as “Charlie.”
A parade of guests presented gifts and citations, then sang his praises.
Dr. Clifford Fagan, Executive Secretary of the National Federation of High School Athletics, attended. State Directors of Athletics from Indiana and Ohio were on hand for the Monday, October 7, 1968, celebration.
Dr. Ira Polly, State Superintendent of Public Instruction, called him “noble, honest and courageous.” John F. Toepp, a state senator and radio sports broadcaster from the Cadillac area, “hailed him as ‘Mr. High School Athletics.’”
Sportswriter Bob Gross, six years into his career at the Lansing State Journal, wrote that Charles E. Forsythe, seated next to his wife Josephine, “only grinned with each word of gratitude.”
More than 350 friends attended the testimonial dinner, honoring the second director of the Michigan High School Athletic Association upon his retirement. For 39 years, Forsythe had served the MHSAA, dedicated to bettering the world of high school sports in Michigan and beyond. His years of service would formulate the mold for those who would follow in his footsteps.
“For five minutes they applauded,” wrote Gross, capturing the moment. Forsythe was humbled by the appreciation. When it was his turn to speak, he thanked the assembled crowd.
 “This is a great night. It’s just wonderful so many of you came to my party. I’m deeply honored,” Forsythe said. “I can’t stand here and accept all the thanks. It was teamwork that made our organization go. And, may I ask of all of you to please help make it grow bigger and better than it is.”
“This is a great night. It’s just wonderful so many of you came to my party. I’m deeply honored,” Forsythe said. “I can’t stand here and accept all the thanks. It was teamwork that made our organization go. And, may I ask of all of you to please help make it grow bigger and better than it is.”
The MHSAA had announced Forsythe’s retirement in late May.
With the exception of a 39-month tour as a Navy Commander, assisting former heavyweight boxing champion Gene Tunney in directing Navy physical fitness activities during World War II, Forsythe had been with the Association since July of 1929, originally as an assistant to Alden W. Thompson, the first director of the MHSAA. (Forsythe remains considered the Association’s first fulltime executive director.)
A graduate and prominent athlete at Milan High School, Forsythe earned his undergraduate degree from Michigan State Normal College (today’s Eastern Michigan University) in 1920 and his Master of Arts degree from the University of Michigan in 1926. He coached basketball and baseball at Milan High School during 1922-23 and taught science. He moved to Lansing Central High School the following year, where he taught history. In the fall of 1926, Forsythe was named director of athletics. According to news reports, he was also “one (of) the leading high school football and basketball officials in the state, working in the district and regional basketball tournaments …”
In his introduction of Forsythe as his new assistant, Thompson said “his presence in this office will make it possible to extend the service rendered by the State Association for the ultimate good of the athletic program throughout the state. The growth of the basketball tournaments, the addition of regional track meets as well as tournaments in tennis and golf, and state association participation in swimming and cross country have all added to the details of business handled through the office of the state director …”
In his book, “Athletics in Michigan High Schools: The First Hundred Years” published in 1950, Lewis L. Forsythe noted that additional help definitely was needed. The elder Forsythe, who was Charles’ uncle, was principal of Ann Arbor High School from 1917 until his retirement in 1946. He twice had served as president of the Michigan Interscholastic Athletic Association, the predecessor to the MHSAA. Elected president of the MHSAA Representative Council in 1924, Lewis Forsythe continued serving in that role until 1942. He had seen, first-hand, Thompson’s need for help.
 “Ever since the new association was organized, it had been the wonder of every informed person that Mr. Thompson could stand up under the strain of the work he felt compelled (or impelled) to do. We knew the strain was terrible and unwise,” Lewis Forsythe wrote.
“Ever since the new association was organized, it had been the wonder of every informed person that Mr. Thompson could stand up under the strain of the work he felt compelled (or impelled) to do. We knew the strain was terrible and unwise,” Lewis Forsythe wrote.
“(Charles’) appointment not only relieved Mr. Thompson of a great deal of detail, but enabled the association to enlarge and improve its services to the schools.”
As assistant director, Charlie traveled Michigan, supervising state officials and conducting MHSAA tournaments. While he was in the office, he improved Association communication with member schools by preparing and expanding the State Association Bulletin. When Thompson was appointed to State Director of Health and Physical Education in Michigan in 1931, it opened the door for Forsythe to become director of the MHSAA.
“Thompson had the job of building the Michigan High School Athletic Association ‘from scratch’ and he built very well,” said Charles several years later. “He was thorough in his application of rules and in seeing that they all were interpreted alike both to large and small schools, so no favoritism or any difference were shown.” If there has been any success in the (years I) served, much of it can be credited to the background and good training I received during the period that I served under Thompson …”
In 1939, Forsythe released the first of four editions of his book, “The Administration of High School Athletics.” It quickly found a home as a textbook at various colleges and universities around the country. For 19 summers, he travelled as a visiting lecturer or staff member of the Universities of Michigan, Wisconsin, Ohio State, Southern California, West Virginia, Indiana, Oregon and elsewhere.
In 1941, George Maskin of the Detroit Times wrote about Charlie’s impact after 12 years in the position.
“This Forsythe fellow is a short, stocky gent of 41. There’s a touch of gray circling around the edge of his head, probably caused by the nights he’s stayed awake worrying whether one of his new ventures would turn out successfully,” Maskin wrote.
“There have been some mighty changes, as well as improvements, since Forsythe was hired to boss the preps. But when he talks, Forsythe speaks in terms of ‘we.’ There’s nothing egotistical about Forsythe’s way of doing things. “
Maskin noted some of the achievements that had occurred under the Forsythe regime. During those dozen years, the number of schools competing in Michigan prep sports jumped from 600 to 750. Six-man football had spread to 100 of Michigan’s smaller schools, which formerly passed over the fall sport. Under Forsythe’s leadership, local and regional tournaments in basketball play increased, “thus reducing the amount of traveling and time lost from school during the state championships.” A team competing in state tournament basketball games would play no more than one game per day – against two in other states adjoining Michigan. Minor sports – tennis, golf, cross country, swimming – had come into their own. Forsythe recognized their value in drawing additional students into athletics and increasing athletic participation. He would take that knowledge with him when he entered the Navy (and would return from the service with an even broader view of their value).
 Yet, perhaps his greatest achievement was his emphasis on safety in sports.
Yet, perhaps his greatest achievement was his emphasis on safety in sports.
In 1937, at the 13th annual MHSAA football rules meeting, “leaders drafted a program to address and demonstrate “techniques intended to make football a safer game for high school boys.” A mandatory rule to require “a three minute warm-up on the practice field before the start of the second half of each game” was put in place. The association had recognized that more serious injuries in football occurred at the start of the second half, because players had rested between periods and weren’t stretching out before resuming play. The creation of an accident benefit plan administered by the MHSAA for the state’s athletes had been discussed for six years, but had failed to engage because of a lack of participation. In December of 1939, it was finally ratified. The plan went into effect with the 1940-41 school year and required schools participating in the program to report all injuries. That led to more accurate data, and, in turn, an increased focus on safety and attention to equipment.
“There has been a decided improvement in the type of equipment worn, especially in football” said Forsythe to Maskin in 1954. “Rules have been written much more with the idea of protecting participants than formerly used to be the case.”
In 1961, Forsythe noted that face guards helped reduce the number of eye injuries and fractured noses. In the fall of 1962 a compulsory mouth guard rule went into effect in football, resulting in a 58-percent reduction in claims filed against the plan for dental injuries.
But at the time of his retirement, it was still apparent that the state basketball tournament was Forsythe’s pride and joy, and the event that allowed the MHSAA to function financially. Attendance at all District, Regional and Final games in 1930 was 126,000. At the time of his retirement in 1968, postseason attendance topped 775,000.
“I remember the time when we used to have to advertise to try to get people to come to our Finals,” said Forsythe to an Associated Press reporter shortly before his final day. “Now they all are automatic sellouts before the games are played,”
Tighter regulation reduced the use of illegal players, as seen in the earliest years of the tournament.
“Some of the coaches used to go out recruiting,” continued Forsythe. “… In the old days, we were more of a police agency. The coaches would try anything they thought they could get by with. Now they generally ask us first or turn themselves in if they discover they are playing a boy who is ineligible.”
“At 69, he still looks fit enough to play running instead of standing guard in any basketball game. He credits this mostly to a strict diet and sensible exercise, such as working in his garden. Forsythe also plans some traveling. “I might take in next year’s basketball finals,” he added with a grin, “If I can get a ticket.”
But a return trip to Michigan State University’s Jenison Field House, home to the MHSAA Basketball Finals since 1940, wasn’t in the cards. The September 1968 issue of the MHSAA Bulletin featured Forsythe on the cover, celebrating his career. In December, he passed away unexpectedly at his Lansing home. The February 1969 Bulletin presented a memoriam, praising his service and “his keen appraisal of athletics, their place in our society and their administration.”
With the August retirement of John E. “Jack” Roberts after 32 years of service, and the appointment of Mark Uyl as executive director, there have been only seven executive directors since the MHSAA was formed in 1924. Beside Thompson and Forsythe, Julian Smith handled the organization between 1943 and 1944 during Forsythe’s military service. Allen W. Bush (1968-78), who served as an MHSAA assistant for eight years to Forsythe, was followed by Vern Norris (1978-86).
 Ron Pesch has taken an active role in researching the history of MHSAA events since 1985 and began writing for MHSAA Finals programs in 1986, adding additional features and "flashbacks" in 1992. He inherited the title of MHSAA historian from the late Dick Kishpaugh following the 1993-94 school year, and resides in Muskegon. Contact him at [email protected] with ideas for historical articles.
Ron Pesch has taken an active role in researching the history of MHSAA events since 1985 and began writing for MHSAA Finals programs in 1986, adding additional features and "flashbacks" in 1992. He inherited the title of MHSAA historian from the late Dick Kishpaugh following the 1993-94 school year, and resides in Muskegon. Contact him at [email protected] with ideas for historical articles.
PHOTOS: (Top) Charlie Forsythe, standing far right, served at Lansing Central at the time of this photo in 1927. (Top middle) Forsythe in 1938. (Middle) MHSAA Executive Director Alden Thompson. (Below) Forsythe. (Photos gathered by Ron Pesch.)
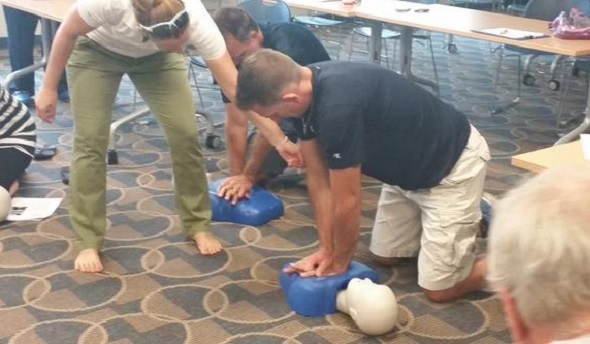
CPR Training, CAP Add to Preparedness
By
Geoff Kimmerly
MHSAA.com senior editor
October 12, 2015
A recent graduate from Ovid-Elsie High School named Chris Fowler started classes this fall at Michigan State University, his days representing the Marauders on the basketball court, football field and golf course now memories as he starts the next chapter of his young adult life.
But his story also will remain a reminder as his high school’s athletic department prepares each year to keep its athletes as safe as possible.
Three years ago next month, Fowler collapsed on the football practice field in cardiac arrest. The then-sophomore was brought back to life by two of his coaches, who revived him with CPR and an AED machine.
There’s no need for athletic director Soni Latz to recount the events of that day when explaining the importance of being ready to respond to a medical crisis – her coaches are well aware of why Fowler survived and understand completely why they too must be prepared.
“Everyone is very aware of what happened and the importance of being trained and knowing what to do, and actually feeling comfortable to step in and administer CPR when needed,” Latz said. “You can feel it’s never going to happen to you, but once it has, it makes you more aware and conscientious to be prepared.”
But Fowler’s story is worth noting on a larger level as varsity coaches at all MHSAA member schools are required this year for the first time to become certified in CPR, and as the largest classes in Coaches Advancement Program history begin course work that includes up to four modules designed to make them aware of health and safety situations that may arise at their schools as well.
The CPR requirement is the most recent addition to an MHSAA thrust toward raising expectations for coaches’ preparedness. The first action of this effort required all assistant and subvarsity coaches at the high school level to complete the same rules and risk minimization meeting requirement as high school varsity head coaches beginning with the 2014-15 school year.
The next action, following the CPR mandate, will require all persons hired as a high school varsity head coach for the first time at an MHSAA member school after July 31, 2016, to have completed the MHSAA’s Coaches Advancement Program Level 1 or Level 2.
In addition, MHSAA member schools this summer received the “Anyone can Save a Life” program, an emergency action plan curriculum designed by the Minnesota State High School League to help teams – guided by their coaches – create procedures for working together during medical emergencies.
“Coaches get asked to do a lot, and even if a school has an athletic trainer or some other health care professional, that person can’t be everywhere all the time. Coaches often are called upon to be prepared for (medical) situations,” said Gayle Thompson, an adjunct assistant professor at Albion College who formerly directed the athletic training program at Western Michigan University and continues to teach CAP sports medicine modules.
“The more (coaches) can learn to handle the situations that can inevitably arise, the better off they’re going to feel in those situations and the better care they’ll be able to offer their athletes. It’s proven that the faster athletes are able to get care, the quicker they’re able to come back to play.”
 Pontiac Notre Dame Prep – which has sent a number of coaches through the CAP program – began a focus on heart safety about five years ago after a student-athlete was diagnosed with a heart issue that allowed her to continue to play volleyball and softball, but not basketball. Athletic director Betty Wroubel said that prior to the student’s diagnosis, the school did provide training in CPR, AED use and artificial respiration; however, that situation put coaches and administrators further on the alert.
Pontiac Notre Dame Prep – which has sent a number of coaches through the CAP program – began a focus on heart safety about five years ago after a student-athlete was diagnosed with a heart issue that allowed her to continue to play volleyball and softball, but not basketball. Athletic director Betty Wroubel said that prior to the student’s diagnosis, the school did provide training in CPR, AED use and artificial respiration; however, that situation put coaches and administrators further on the alert.
Her school offers CPR training also to subvarsity and middle school coaches, using a combination of video instruction from the American Red Cross and in-person guidance by members of the school community who are certified to teach those skills. Students at the school also have received training – and it paid off a few years ago when one of them gave CPR to a baby who had stopped breathing at a local shopping mall.
Portage Central scheduled two sessions this fall for its coaches to receive not only CPR certification, but AED training as well. Central was fortunate to have an American Red Cross first-aid trainer in house, teacher Rachel Flachs, who also is close to the athletic side as the girls swimming and diving coach at Mattawan High School.
Central athletic director Joe Wallace said the training was offered not just to varsity head coaches, but every head coach on every level of the program so that “at least we know that at every given practice, every game, we’d have someone recently trained,” he said.
And he was proud of how his coaches immersed themselves in the subject matter.
“They were putting themselves in scenarios to see how it related to their own sports and asking really great questions,” Wallace said. “It was thought provoking.”
The CAP sports medicine modules are designed to do the same as coaches consider the medical situations they could face. They aren’t designed as “medical training,” said Tony Moreno, a professor of kinesiology at Eastern Michigan University and teacher of all four CAP sports medicine modules. Rather, attendees receive an awareness and basic education on common injuries, injury mechanisms and prevention, and how to create an action plan in the event of an injury incident.
The CAP program touches on a variety of safety topics in several of the available seven levels of coach education.
CAP 1 – which is part of the mandate for new coaches beginning next school year – includes “Sports Medicine and First Aid.” Cap 4 has modules titled “Understanding Athlete Development” and “Strength and Conditioning: Designing Your Program.” CAP 5 includes the session, “Peak Health and Performance.” Attendees also have the option of receiving CPR and AED training as an addition to some courses.
With a quick Internet search, coaches have no trouble finding a variety of resources on sports medicine, performance enhancement, nutrition and healthy living regarding young athletes. “However, some of these sources are more credible and scientifically-based in comparison to others,” Moreno said. “CAP strives on an annual basis to continue to update and improve the quality and credibility of this information and in a face-to-face manner where coaches have the opportunity to ask questions about their experiences and specific programs.”
“Having the CAP requirement will only make them better informed. Many have had this kind of information before, but there’s always something new coming,” Thompson added. “I think we do a good job, not of trying to tell them they were wrong, but maybe taking what they’ve known a step further and making them better prepared – empowering them to do their best.”
Wroubel may understand more than most athletic directors the growing list of tasks coaches are asked to accomplish; she’s also one of the winningest volleyball and softball coaches in MHSAA history and continues to guide both Fighting Irish programs.
But she and Wallace both said the CPR mandate isn’t considered another box to check on a to-do list; there’s enthusiasm because of its importance and the opportunity to carry those skills into other areas of community life as well.
Wroubel has served as a coach since 1975 and said this renewed emphasis on coaches having knowledge of sports medicine actually is a return to how things were when she started. Back then, coaches were responsible for being that first line of medical know-how, from taping ankles to providing ice and evaluating when their athletes should make a trip to the doctor’s office.
“When I first started coaching, we didn’t have sports medicine people, trainers, or team doctors other than for football. You did everything yourself,” Wroubel said. “I think everybody got away from that, but I think it’s coming back because a trainer can’t be everywhere.
“It’s healthy and it’s good for kids. … The more of us with emergency skills, the better we’re able to serve our community.”
PHOTOS: (Top) Portage Central coaches receive CPR training earlier this fall. (Middle) Pontiac Notre Dame Prep coaches practice during AED training. (Photos courtesy of school athletic departments.)

