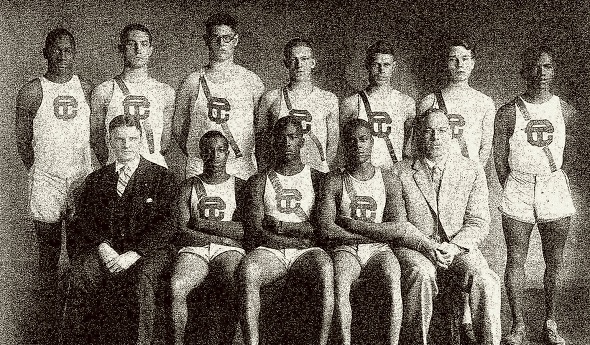
'Midnight Express' Got Start at Cass Tech
April 11, 2017
By Ron Pesch
Special for Second Half
If Eddie Tolan had his way, he might have been a football hero or, maybe, a star on the baseball diamond. But fate is a funny thing.
Instead, he became an Olympic track star and, one can strongly argue, the Michigan High School Athletic Association’s greatest athlete of all-time.
A heart attack took him early, at the age of 57 in late January, 1967. His kidneys had failed him two years prior, and were the primary reason for his early death. Easily recognizable by his horn-rimmed glasses, Tolan would inspire generations of athletes during his lifetime and in the years that followed. Recognition for his accomplishment, via induction to Halls of Fame, would mostly arrive after he departed.
“Eddie was just Eddie,” said his youngest sister, June, “very humble and gentle. He enjoyed meeting and knowing other people, and was loved by children.”
Born Thomas Edward Tolan, Jr., in Denver in 1908, Eddie and his family moved to Salt Lake City when he was young. His father, a hotel cook, then moved his wife and their four children to Detroit when Eddie was 15. Stories of opportunity for African-Americans had prompted the move.
Within the family, Eddie’s older brother, Hart, his senior by a year, was considered the better athlete.
“Only Hart neglected to train,” said sister Martha. “Eddie was a worker.” His mother, Alice, simply described Eddie as more determined.
Following in the footsteps of his brother, Eddie joined the football team at Detroit Cass Technical High School in the fall of 1924. A sub on the squad, Eddie emerged as the team’s quarterback in the fall of 1925 under the school’s new football coach, William Van Orden. Although Eddie stood only 5-foot-4, he threw a beautiful pass. He was also lightning fast, light, and evasive. It was here, on the football field, that it seemed he would find stardom.
 While the team saw limited success in the early going, Eddie quickly emerged as the star. He scored the lone touchdown in the Mechanics’ 12-6 season-opening loss to Detroit Southwestern. Held scoreless in the second game of the season, Cass Tech tied Southeastern, 6-6, in the season’s third game. The next week, the team exploded for 47 points, shutting out the Detroit Western Cowboys in “one of the biggest upsets of the current season,” according to the Detroit Free Press. Tolan accounted for four of Cass Tech’s seven touchdowns. His brother, Hart, also scored that day. Despite what the future held, it was the moment he would always rank as his favorite among his athletic achievements. Football was Eddie’s favorite sport, followed by baseball.
While the team saw limited success in the early going, Eddie quickly emerged as the star. He scored the lone touchdown in the Mechanics’ 12-6 season-opening loss to Detroit Southwestern. Held scoreless in the second game of the season, Cass Tech tied Southeastern, 6-6, in the season’s third game. The next week, the team exploded for 47 points, shutting out the Detroit Western Cowboys in “one of the biggest upsets of the current season,” according to the Detroit Free Press. Tolan accounted for four of Cass Tech’s seven touchdowns. His brother, Hart, also scored that day. Despite what the future held, it was the moment he would always rank as his favorite among his athletic achievements. Football was Eddie’s favorite sport, followed by baseball.
With the goal of avoiding injury and damage to Detroit’s prep gridirons, a heavy five-hour downpour on Saturday, Oct. 24 meant Cass Tech’s game with Hamtramck was rescheduled for Monday the 26th at Northwestern High School.
Despite the delay, the teams squared off on a field that was in worse condition than it had been Saturday. Early in the first quarter, the heavier Hamtramck squad dashed Cass Tech’s hopes for a shot at contending for the Detroit Public School League crown. Thrown for a four-yard loss, Eddie Tolan “was left lying in the mud, the victim of several torn ligaments.”
Cass Tech lost the game, 12-0, and Eddie Tolan was lost for the season.
“Rated as one of the best forward passers in the city, Tolan combined all the qualities of a first class quarterback,” noted the Free Press a few days later, “and his loss is a death blow to the chances of Cass finishing near the top.”
In spite of the injury, Eddie had been impressive enough to be named quarterback on the paper’s All City third-team squad at season’s end.
He would never return to the gridiron.
Birth of a legend
Back in the 1920s, winter meant indoor track for preps. It was the age of dynasties, where the sport at a team level was ruled by the public schools of Detroit, and one school in particular – Detroit Northwestern. The Colts had won four of the last five indoor city meets as the public schools entered the 1925 track season, and they would again reign that spring.
As it remains today, skill was needed across both track and field events to dominate as a team. Still, there was room for individuals to shine. Tolan arrived on the track scene during this time, and as a sophomore, showed early promise.
It was the golden age of athletics, as well as newsprint. Today it’s hard to imagine a time when track headlines could snake their way to the top of the sports page of a big city newspaper, highlighting the accomplishments of the local preps. Yet in the 1920s and 1930s, that was the case. Tolan earned two spots in the annual city meet in 1925, appearing in the 30 and 220-yard dashes. While he failed to place among the leaders in the furlong, Eddie did finish fourth in the 30-yard dash, behind three runners from Northwestern, including Charles “Snitz” Ross, the winner of the event and the city’s emerging sprint star. Unfortunately, Tolan’s finish was disqualified, as he had run out of his lane.
 On March 20 and 21, the first indoor interscholastic track and field meet was hosted at the University of Michigan. The two-day event featured 20 in-state schools, and a pair from outstate – Waite High of Toledo and Austin High of Chicago. A total of 185 athletes showcased the university’s newly opened Yost Fieldhouse while competing in 12 events. The competition was ruled by Detroit Northwestern, with first-place finishes in eight of the events and a total of 51½ points. Cass Tech finished a distant second with 14 points. Tolan earned a second place in the 50-yard dash, behind Ross of Northwestern, the winner of the race.
On March 20 and 21, the first indoor interscholastic track and field meet was hosted at the University of Michigan. The two-day event featured 20 in-state schools, and a pair from outstate – Waite High of Toledo and Austin High of Chicago. A total of 185 athletes showcased the university’s newly opened Yost Fieldhouse while competing in 12 events. The competition was ruled by Detroit Northwestern, with first-place finishes in eight of the events and a total of 51½ points. Cass Tech finished a distant second with 14 points. Tolan earned a second place in the 50-yard dash, behind Ross of Northwestern, the winner of the race.
Eddie’s skills continued to bloom during the outdoor season, which began in April. There, the sophomore excelled in the 100 and 220 events. A breakout performance at a late-season triangular meet with Northwestern and Southwestern, where Eddie defeated Ross in the 100-yard, caught the attention of many. His time of 10.2 seconds tied the city record, established by George “Buck” Hester of Detroit Northern in 1922. Born in Windsor, Ontario, Hester had competed for Canada in the 1924 Olympics, hosted in Paris. He would run collegiately at the University of Michigan.
At the same meet, Tolan topped the city mark in the 220-yard dash, covering the distance in 23.1 seconds.
Less than a week later, Ross toppled the century mark, with a 10.1 in the preliminaries to the city’s outdoor meet. A rivalry, bubbling at the surface, now exploded.
Anticipation for the showdown between Ross and Tolan at the city finals in the 100 was met with disappointment among fans, as Tolan won the race with a spurt in the final three steps to the wire, posting a 10.4 time, while Ross finished fourth. Tolan also won the 220 while Ross did not place. John Lewis of Northeastern finished second in both events.
 Junior William Loving of Cass Tech emerged as the city’s outstanding performer, “taking first place in the high jump, and both hurdles, aside from running in the relay and finishing third in the discus,” that Saturday, May 16 at Codd Field. The performances still were not enough to unseat Northwestern, the winner of the meet.
Junior William Loving of Cass Tech emerged as the city’s outstanding performer, “taking first place in the high jump, and both hurdles, aside from running in the relay and finishing third in the discus,” that Saturday, May 16 at Codd Field. The performances still were not enough to unseat Northwestern, the winner of the meet.
Northwestern also won the 25th Annual Outdoor meet at the University of Michigan. Loving finished as the high point winner at the event, while Tolan tied with Lewis of Northeastern for second in the century dash, behind Jimmy Tait of Northwestern. Ross finished fourth.
Beginning with their victory in 1920, Northwestern also ruled the annual state track championship in East Lansing, clinching the Class A title in four of the previous five years under the guidance of Bert Maris. (The 1922 Class A title was won by Detroit Northern).
At the first championship sponsored by the newly formed Michigan High School Athletic Association, the result was the same. This time, Maris was assisted by Warren Hoyt, and it took a prep “world’s record in the 880 relay” to top Cass Tech. Northwestern ended the day with only three first-place finishes. Team depth had allowed Colts to win the meet with 38 points against 34 2/3by the Mechanics.
Cass Tech’s Loving ended the day with the top point total for an individual, with 12½, while his teammate Tolan added 10 points, by winning both the 100 (10.1) and 220-yard (22.4) dashes. While expected to do well, the sophomore was still an underdog in each event. Lewis again finished second in both events, while Tait landed third place and Ross finished fourth in the 100.
The injury, and a reminder
Following the football injury, Tolan was still unable to perform in January when the 1926 indoor track season opened. However, the high school junior was back in February in time for the Mechanics’ dual meet with Northwestern. Sporting a bandage on his left knee, Tolan topped Ross in the 30-yard dash. The bandage, covering the knee, would remain with him for the rest of his running career, symbolic of that return victory.
Hopes ran high that Cass Tech might challenge the Colts for the city’s indoor title in 1926, but it didn’t turn out that way. Northwestern again dominated the city’s seventh annual meet, winning five of the day’s first nine events. Ross and Tolan tied at the tape in the 30-yard dash, but the run was tainted. Ross’ “eagerness to outsprint Tolan, his most bitter rival,” resulted in two false starts, and Ross was set back two feet to begin the race. Without the penalty, there was little doubt that Ross would have won the event cleanly.
At the Second Annual Indoor Interscholastic, held at Yost Fieldhouse on March 20, George Simpson of East Columbus, Ohio, grabbed the 50-yard dash crown. Ross earned second in the race, while Tolan finished fourth. Detroit Northwestern again won the invitational, but this time in less-dominating fashion, as the field of participating schools was greatly expanded.
Multiple Detroit athletes were selected to compete at the prestigious Northwestern University Indoor prep invitational, scheduled for the following week in Evanston, Ill. Loving finished as high point scorer of the meet with 11, with a win in the 60-yard high hurdles and second-place finishes in the low hurdles and high jump. Combined with Tolan’s second-place finish in the 50-yard dash, the pair totaled 14 points, enough to win the event. Cass Tech’s return to Detroit as champion was loudly trumpeted in the press.
Based on the performance at the national level, the Mechanics were identified as strong candidates to dethrone the Colts during the upcoming outdoor season. Despite strong results at duals and triangular meets, Cass Tech still fell to Northwestern in total points at the annual city carnival.
Finally, a team victory
At the 26th annual University of Michigan outdoor interscholastic meet, Cass Tech scored its biggest triumph, surprising “the best of the schoolboy athletes from Detroit, Toledo and Chicago, without mentioning stars from the states of Michigan, Ohio, Illinois and West Virginia at large.” Amazingly, Kalamazoo Central also slipped past Detroit Northwestern in the standings. The Colts had to settle for a third-place finish at Ann Arbor.
While rain and cold temperatures meant record performances were few, Tolan won the 100, over Jimmy Patterson of Chicago Tilden Tech (winner of the 50-yard indoor race at Northwestern University earlier in the spring), Lewis of Northeastern and Ross of Northwestern, with a time of 10.3. His 22.1 seconds in the furlong topped Patterson, Edgar Fenker of Kalamazoo Central and Lewis, respectively.
Of course the Colts were expected to find redemption at the 20th annual state track and field meet, scheduled for May 28 and 29 at Michigan State College. As expected, both Northwestern and Cass Tech, along with Kalamazoo Central did well at the preliminaries. Yet, in a stunning turn of events, the finals mimicked that of a week before with Cass Tech, guided by Coach Van Orden, winning the Class A state title, followed by Kalamazoo Central, then Northwestern. Loving and Tolan were the stars of the event. Tolan “romped” in the 100 and 220 dashes, while Loving, now a senior destined for Western State Teachers College, repeated as winner of both the high and low hurdles.
Graduation gutted Cass Tech’s track roster, and by the time of the indoor city meet in 1927, only Tolan remained to take on Northwestern’s juggernaut. Jack Dant of Northwestern surprised everyone with a new city record in the furlong, with a 24.7 in the preliminary of the city meet. The mark would stand as the city indoor record for 24 years until topped in 1942. In the finals, Tolan grabbed top honors in the 30-yard dash and finished second in the 220. Dant placed fourth, with each runner trailing Edward Swan, captain of Northwestern. The Colts again reigned as city champions. Two weeks later on the 19th, Tolan won the 50-yard dash at the Third Annual Indoor event at the University of Michigan. At Northwestern University’s national indoor championships on March 26, he won the 50, running the distance in 5.3 seconds.
 Tolan’s star shined brightest during the outdoor season. On May 14th at the University of Michigan’s annual outdoor interscholastic, Tolan won the 100 and 220 dashes. On the 22nd, he captured the same two events at the city’s outdoor meet.
Tolan’s star shined brightest during the outdoor season. On May 14th at the University of Michigan’s annual outdoor interscholastic, Tolan won the 100 and 220 dashes. On the 22nd, he captured the same two events at the city’s outdoor meet.
One week later, for the first time in history, all four classes of Michigan high schools met for the state championships in East Lansing. Favored to win, Tolan closed out his career by matching Hester’s record time of 9.8 seconds in the 100 – a mark thought unattainable. With little rest, he then fought off Kalamazoo’s Fenker in the 220, winning by a stride with a time of 21.9. The victories meant Tolan was undefeated in each event over his three years running at the MHSAA state championships.
Northwestern returned as team champion, this time coached by Malcolm Weaver. Outside of back-to-back team victories in 1916 and 1917 by Grand Rapids Central, the Class A crown had been possessed by Detroit schools in 11 of the past 14 years. (No meet was run in 1918 due to World War I.)
Tolan wrapped up his high school career at the University of Chicago. One of 14 Detroit area athletes invited to the Interscholastic Track Championships, Tolan equaled the prep world’s record time of 9.8 seconds in the 100-yard dash, then grabbed the furlong, topping runners from Minnesota, Iowa, Illinois and Indiana.
Accurate or not, news spread from coast-to-coast via the media wire of Tolan’s track skill, noting he had won 17 out of 18 city and state outdoor championships in three years of prep competition.
As a junior, Tolan had run Amateur Athletic Union track, sponsored by the Detroit Department of Recreation in the summer, and he returned to AAU competition following graduation, running against active and former college track luminaries. At the state track championships at Belle Isle on July 4, Tolan starred. Running for the Detroit Athletic Association team, he won the 100 and 220, topping Victor Leschinsky, former University of Michigan sprinter.
Next stop: Ann Arbor
While enrolled at U-M, in January of 1928, Tolan was named a 1927 High School All-American by the AAU. At Michigan, he earned the nickname “Midnight Express” and began to chew gum while racing.
As a sophomore, Tolan tied the world’s record in the 100-yard dash, laying down a 9.6-second time at the Western Conference preliminaries at Evanston, Ill, against George Simpson, a former prep opponent from Columbus, Ohio, now running for Ohio State. One day later, on May 25, 1929, at Duche Stadium at Northwestern University, Tolan bested the mark.
With a slight breeze at the runners’ backs, Tolan came from behind, and “with his big horn-rimmed spectacles firmly taped to his head, electrified the crowd by winning the 100-yard dash in :09.5 seconds. He beat Simpson to the tape in an eyelash finish that was inconceivably close.”
These were the days when starting blocks were still not accepted for official races. It took a year before the International Amateur Athletic Association pronounced the mark as the new world’s record.
By college graduation, Eddie had run the 100 a total of 143 times for the Wolverines, losing the race on only nine occasions.
An Olympic hero
While the participants and witnesses have been silenced by father time, their voices gone thanks to the ailments that arrive as we age, Tolan’s exploits at the 1932 Olympics have been well recorded.
After graduation, Tolan and the nation’s top sprinters traveled North America, racing in preparation for the Olympic trials. When they finally arrived, he was beaten by Ralph Metcalfe of Marquette University in both the 100 and 200-meter races. Still, the top three times qualified, and both men, along with old rival George Simpson, made the Olympic roster.
 It was a time where the press was very cognizant of skin color and quick to note that this was the first time that the top two individual sprinters representing the United States were African-American. At the games, staged in Los Angeles, Tolan became the first African-American to receive the title “world’s fastest human” when he edged Metcalfe in the first-ever photo finish in the 100-meter race, and then earned a second gold with victory in the 200-meter event. His time in the 100 would remain an Olympic record until 1960.
It was a time where the press was very cognizant of skin color and quick to note that this was the first time that the top two individual sprinters representing the United States were African-American. At the games, staged in Los Angeles, Tolan became the first African-American to receive the title “world’s fastest human” when he edged Metcalfe in the first-ever photo finish in the 100-meter race, and then earned a second gold with victory in the 200-meter event. His time in the 100 would remain an Olympic record until 1960.
Tolan returned to Detroit to a hero’s welcome when his train arrived at Michigan Central Station in late August. The acclaim continued at city hall, then at the Brewster Recreation Center, where he celebrated with friends and family. September 6, 1932, was declared “Eddie Tolan Day” by Michigan governor Wilber Brucker.
This country was in the depths of the Great Depression, and opportunity for all Americans was limited. But while his had become plentiful, Tolan had no plans to “cash in” on his fame, and he expected to remain an amateur.
For a short time following the games, he joined Bill “Bojangles” Robinson on the vaudeville circuit. There, he described his Olympic success to attentive crowds. It was ruled that the venture violated his amateur status. In 1933, with both his father and brother out of work, Tolan found employment as a filing clerk in the register of deeds office of Wayne County. In 1934, he was offered a chance to race professionally in Australia. Following a six month barnstorming tour, he returned home, resuming his position with Wayne County.
In 1937, he was appointed to Michigan’s National Youth Administration, where he assisted other African-Americans with vocational guidance and placement. He continued to support his parents financially. In his final years he worked as a physical education teacher in Detroit.
A bachelor all his life, in 1954 Tolan lost his mother to old age. Later in the year, he was named to a roster of 22 all-time greatest U.S. Olympians. In 1958, he was inducted into the Michigan Sports Hall of Fame along with five others. Only 12 names had preceded the group, and Tolan was just the second African-American honored by the Hall.
“Oh, man, it was a terrible thing,” said Jessie Owens, four-time U.S. gold medalist at the 1936 Olympics, discussing the loss with Jet magazine at the time of Tolan’s death in January 1967. “When I was in high school, Eddie and Ralph (Metcalfe) were my idols. Eddie and I later became close friends. I used to live in Detroit, and every time I’d go back Eddie was one of the first ones I’d look up.”
Posthumously, in May 1967, a 17-acre playground on Detroit’s east side, near the Children’s Hospital of Michigan, was dedicated with his name. An artificial kidney machine, purchased for Wayne County General Hospital with funds raised by his sisters, was donated in his honor in 1969.
Eddie was inducted into the University of Michigan’s Athletic Hall of Honor along with 10 others at the university’s third induction in 1980 and was added to the National Track and Field Hall of Fame along with its ninth class in 1982. Today, medals and a pair of his track shoes, donated by his sister, June Tolan Brown, are on display at the Charles H. Wright Museum of African American History in Detroit.
 Ron Pesch has taken an active role in researching the history of MHSAA events since 1985 and began writing for MHSAA Finals programs in 1986, adding additional features and "flashbacks" in 1992. He inherited the title of MHSAA historian from the late Dick Kishpaugh following the 1993-94 school year, and resides in Muskegon. Contact him at [email protected] with ideas for historical articles.
Ron Pesch has taken an active role in researching the history of MHSAA events since 1985 and began writing for MHSAA Finals programs in 1986, adding additional features and "flashbacks" in 1992. He inherited the title of MHSAA historian from the late Dick Kishpaugh following the 1993-94 school year, and resides in Muskegon. Contact him at [email protected] with ideas for historical articles.
PHOTOS: (Top) The 1926 Detroit Cass Tech track & field team was led by a handful of standouts including the emerging Eddie Tolan. (Middle top) Tolan, in 1925. (Middle) Detroit Northwestern standout Charles Ross. (Middle) Bill Loving, also a Cass Tech star. (Middle below) The program cover from the 1927 MHSAA Track & Field Finals. (Below) Tolan after the World Professional Sprint Championships in Melbourne, Australia, in 1935. (Photos collected by Ron Pesch with assistance from Detroit Cass Tech's Regenia Kirk.)

The Last Time MHSAA Finals were Canceled
By
Ron Pesch
MHSAA historian
April 27, 2020
Historians trace the start of World War II to German dictator Adolph Hitler’s decision to invade Poland on September 1, 1939. The Empire of Japan’s involvement in the war became effective in September 1940 with the signing of the Tripartite Pact.
Until December 7, 1941, the United States avoided official involvement, declaring themselves “a neutral nation.” Then came Imperial Japan’s bombing of Pearl Harbor.
A labor shortage caused by World War I had taken out spring high school sports in Michigan in 1917. As noted in the Second Half article, “1918 Pandemic, WWI Threatened High School Sports,” the global spread of a devastating strain of influenza interrupted the football season in Michigan. Prep athletics would roar through the 1920s and survive the Great Depression before seeing another interruption.
That next disturbance had nothing to do with war’s insatiable desire for manpower. Rather, it was because of tires.
“When the Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor, rubber instantly became the most critical strategic material for making war,” wrote Stephen W. Sears in the October/November issue of American Heritage magazine in 1979. “Nine-tenths of the nation’s rubber came from the Far East, and it was painfully evident that nothing would now stop Japan from cutting off that source.”
Americans consumed nearly two-thirds of the world’s production of rubber. With only about a year’s worth of material on hand, “Just four days after Pearl Harbor a freeze was put on the sale of new passenger-car tires,” stated Sears, “and on December 27 tire rationing was authorized, to go into effect early in January, 1942. Sales of new cars also were halted.”
The MHSAA
The Michigan High School Athletic Association arrived in December 1924. It replaced the old Michigan Interscholastic Athletic Association which had served Michigan for 15 years.
The organization’s primary purpose was to standardize, interpret and administer rules, educate and guide officials, and regulate student eligibility within prep sports in Michigan. By the 1940s, it had evolved into an association that also managed postseason tournaments, designed to identify state champions in specific sports: swimming, cross country, golf, tennis, track, and the sport sponsored by the most high schools in the state, basketball.
 “The old MIAA had taken over the regulation of basketball tournaments in 1920. This had been done as a service to the schools and especially as a means of eliminating evils inherent in the invitational tournaments (that were hosted by various colleges around the state and the midwest),” wrote Lewis L. Forsythe in his book, Athletics in Michigan High Schools, recalling the first 100 years of prep sports in the state.
“The old MIAA had taken over the regulation of basketball tournaments in 1920. This had been done as a service to the schools and especially as a means of eliminating evils inherent in the invitational tournaments (that were hosted by various colleges around the state and the midwest),” wrote Lewis L. Forsythe in his book, Athletics in Michigan High Schools, recalling the first 100 years of prep sports in the state.
“In the last days of February 1942,” multiple Michigan schoolmen were in San Francisco to attend the annual meetings of Secondary School Principals, Superintendents and the National Federation of State High School Associations. “We were well aware that many of our boys in school would have to offer themselves in the service of their country,” noted Forsythe in his publication. “We fully realized that the quality of that service and, indeed, their own survival might well depend quite as much on their physical fitness as on their intellectual and spiritual resources. It was under those circumstances that we determined so to modify the emphasis of our athletic program as to make the largest possible contribution to the war effort. We recognized that the need in Michigan could not be met by our organization alone, and we therefore determined to encourage a general enrollment of all school groups in a united effort for promotion of physical fitness.”
Because of the “scarcity of tires and automobiles,” in April 1942 the MHSAA announced plans to curtail their upcoming annual golf and tennis events, eliminating a state championship round. Instead, the seasons were concluded with separate eastern and western sectional tournaments, hosted in Ann Arbor and Grand Rapids.
Early in May of 1942, MHSAA executive director Charlie Forsythe, nephew of Louis Forsythe, announced that the Association was “working on plans designed to make body-building exercises available to more young men and to spread recognition of sports achievements. He predicted substantial growth of intramural sports to include youngsters whose limited prowess might keep them from such interscholastic sports as football, baseball or basketball.”
Wire articles had told the story of how the running Battle of the Atlantic had impacted U.S. ocean transportation along the eastern seaboard. A Germany-mounted “campaign against American coastal shipping” by U-boats (submarines) was devastating “a section of America almost exclusively dependent upon ocean-point tankers for its petroleum products.” Without a viable alternative means to transport the products, on May 15, 1942, gasoline rationing began in 17 seaside states and the District of Columbia. It was hinted that gas rationing – specifically designed to save rubber – could roll out nationally. (Crude oil is the main ingredient in man-made rubber.)
The chances for restrictions in Michigan were a distinct possibility. According to P.J. Hoffmaster, the state’s supervisor of wells, the state consumed approximately 140,000 barrels of oil per day, but produced only 64,054 barrels. “This state has a shortage of at least 100,000 barrels on the basis of a regional demand,” he said, noting Michigan oil also supported needs outside the state. “When people say there can’t be rationing in Michigan because we have plenty of our own oil, they don’t have the true picture.”
Reverberations begin
When quizzed on the subject before the annual Lower Peninsula Track and Field championships, hosted at Michigan State College in May 1942, (Charlie) Forsythe, told The Associated Press he was unsure how rationing might affect the Association’s annual playoffs.
 “It is too early as yet to say exactly. … We are making every effort to maintain an adequate athletic program. Certainly where common carriers (busses and trains) will make it possible to get a team to a game, that means should be used,” Forsythe said. He added that the Association was “surprised to find the number of schools competing in this year’s tournaments practically equaled last year’s entries.”
“It is too early as yet to say exactly. … We are making every effort to maintain an adequate athletic program. Certainly where common carriers (busses and trains) will make it possible to get a team to a game, that means should be used,” Forsythe said. He added that the Association was “surprised to find the number of schools competing in this year’s tournaments practically equaled last year’s entries.”
A total of 162 schools had qualified individual contestants in the track championships, about 10 percent fewer than in 1941. However, L.L. Frimodig – the assistant director of college athletics at M.S.C. and acting director of the state track meet – felt “the actual field in the four-class carnival would be much smaller than the number eligible to compete,” considering the circumstances of travel. “Many coaches,” he said, “would think in terms of tires rather than trophies before embarking on any sizable journey to the meet.”
The threat of rationing was almost immediately seen within Michigan’s resorts and travel industry.
“July and August have been moved up into June,” wrote the Detroit Free Press. “This is the word that comes from various parts of the state. Evidently, determination to get the vacation over before gas rationing may be decreed is one of the factors that has stepped up the season. … Reports of heavy patronage at nearby resorts over Memorial Day week-end can be taken as an indication of the trend, or necessity in 1942 of holidays enjoyed close to home base.”
Come September, Joseph B. Eastman, national director of the office of war transportation, called for help in reducing consumption of natural resources: “We intend to solicit the help of colleges and universities in making arrangements for transfer of scheduled games to centers of population where as many people as possible will have an opportunity to attend football games without traveling.”
At the college level, the freshman eligibility rule was waived due to the loss of manpower tied to military enlistment and the enactment of the Selective Training and Service Act of 1940. Its passage required all men between ages 21 and 45 to register for the first peacetime draft in U.S. history. With entry into the war, in December 1941, it was amended to require all 18 to 64-year-olds to register, with starting age for likely draft lowered to 20.
“The seasons of 1942-45 turned the (college) game upside down, creating new juggernauts and decimating some old ones,” wrote Sports Illustrated in its 1971 article, “When Football Went to War.”
 “Michigan’s 85 high school athletic leagues are speculating on the effects of the office of defense transportation plan to whittle sports travel drastically,” stated an Associated Press (AP) article soon after Eastman’s announcement. The Southwestern Conference, comprised of Kalamazoo Central, Benton Harbor, Muskegon, Holland, Grand Haven and Muskegon Heights and one of the most widely spread major prep circuits in the state, was told by its regular bus company that its busses were not available for charter.
“Michigan’s 85 high school athletic leagues are speculating on the effects of the office of defense transportation plan to whittle sports travel drastically,” stated an Associated Press (AP) article soon after Eastman’s announcement. The Southwestern Conference, comprised of Kalamazoo Central, Benton Harbor, Muskegon, Holland, Grand Haven and Muskegon Heights and one of the most widely spread major prep circuits in the state, was told by its regular bus company that its busses were not available for charter.
On Sept. 25, according to AP, “the state department of public instruction warned today that a threat of ‘no new tires’ will be held over rural schools which use their school busses to transport football players to and from games.”
Julian W. Smith, named the interim director of the MHSAA when Charlie Forsythe went into military service, didn’t think the directive would have much impact on football schedules. “However, I believe the order will have a serious effect on basketball schedules this winter and on next year’s football schedule.”
“Four Gallons a Week for Most Drivers”
Two days later it was announced that nationwide gas rationing would go into effect at the beginning of December 1942. More immediately, compulsory tire inspections every 60 days and a “Victory Speed Limit” of 35 miles per hour, effective Oct. 1, were also enacted. “This is not a gasoline rationing program, but a rubber conservation program,” said William M. Jeffers, president of the Union Pacific Railroad, which had been placed in charge of the government’s struggle to alleviate the rubber shortage.
“The object is not to take cars off the road, but to keep them on the road. … The safe life of a tire at 50 miles per hour is only half as great as it is at 30 m.p.h.”
 After initial announcements of game cancellations, the impact on high school football in Michigan in 1942 appears to have been minimal. Solutions were found to most challenges. In Bessemer, the high school superintendent announced that “enough persons have volunteered their automobiles to take the Speed Boy players to Calumet” for the game, scheduled for Saturday, Oct. 3. At season’s end, Flint Northern, Detroit Catholic Central, Muskegon, and Wyandotte each lay claim to a share of Michigan’s mythical football title.
After initial announcements of game cancellations, the impact on high school football in Michigan in 1942 appears to have been minimal. Solutions were found to most challenges. In Bessemer, the high school superintendent announced that “enough persons have volunteered their automobiles to take the Speed Boy players to Calumet” for the game, scheduled for Saturday, Oct. 3. At season’s end, Flint Northern, Detroit Catholic Central, Muskegon, and Wyandotte each lay claim to a share of Michigan’s mythical football title.
But a hint of what was to follow came with an announcement concerning the annual Cross Country Finals. The state meet was cancelled to reduce travel, with honors instead awarded during October meets to which schools were assigned based on geography.
In its October 1942 bulletin, the MHSAA endorsed a commando-type “training plan drafted by the Minnesota branch of the office of civilian defense” to “step up scholastic physical fitness programs.” When plotted on a football field, the course bordered the playing area with 11 obstacles spaced 20 yards apart. The course required participants to jump a 4-foot fence, crawl under a 2-foot-high rope, then run between a maze of stakes and, later in the course, high-step through a series of open boxes. Students would scale a 7½-foot wall, walk on a 12-foot balance beam, swing across a broad jump pit from a rope that hung from above, then climb another rope hung from the crossbar of the goal posts. Once accomplished, the participant was to move, hand-over-hand, across the span of the crossbar before dropping to the ground.
At the end of October, the MHSAA’s Representative Council acknowledged the direct contribution that interscholastic sports had on the “lives of students and citizens of the communities in which they are offered” while recommending that they be “retained insofar as possible.”
The committee, however, also emphasized its belief “that physical fitness programs for all students, and intramural sports to offer opportunity for competition to all, should be stressed in the schools’ athletics program.
“In all probability,” it continued, “it will be necessary to modify the general plans of conducting tournaments.” The mechanics of modification would be hammered out at the next Council meeting to be held in December in Lansing.
Financial concerns also were expressed, as much of the Association’s operating budget came from a share of gate receipts of tournaments.
The Impact
“All over the state, athletic directors and coaches are tackling transportation problems. Instead of piling the athletes into privately owned automobiles or school busses, coaches have diligently studied timetables of regular train and bus lines with many satisfactory results,” stated the AP on Dec. 4.
That same day, the MHSAA announced that the upcoming basketball postseason would be altered due to rationing. The story was picked up by various newspapers across the Midwest.
“The association’s Representative Council last night stressed need for following a ‘principle of minimum travel’ in basketball play this winter and voted to dispense with the annual Lower Peninsula finals,” instead opting for a modified layout. Initial conversation related to a plan calling for sectional meets with the possibility of naming titles in the northern half of the Lower Peninsula, and in both the southern and eastern areas. An appointed basketball committee was also to consider combining enrollment classifications wherever necessary to localize tournament play.
From 1932-1947, inclusive, separate Lower and Upper Peninsula basketball champions were determined. The Upper Peninsula Athletic Committee announced a similar plan at its meeting in January of 1943. The committee expected to present winners of the U.P. events with certificates instead of the customary trophies due to shortage of materials prompted by the war.
According to a survey of its 40 member state associations by the National Federation of State High School Associations, Michigan was one of only four states, including Maine, Montana and Nevada, to eliminate naming basketball state champions come the winter of 1943, “since the distances within those states are too vast or transportation facilities are too limited. The same will prevail in track contests.”
 By mid-January, the MHSAA had polled its membership, and approximately 95 percent of the state’s high schools indicated a desire to participate in the replacement tournaments pitched by the Association. After examining the logistics, the plan previously discussed was modified. The Association then identified 51 Lower and 11 Upper Peninsula sites, based on availability to host the tournament and geographic suitability. The competition would run for two weeks, and end with what had previously equaled District championship contests.
By mid-January, the MHSAA had polled its membership, and approximately 95 percent of the state’s high schools indicated a desire to participate in the replacement tournaments pitched by the Association. After examining the logistics, the plan previously discussed was modified. The Association then identified 51 Lower and 11 Upper Peninsula sites, based on availability to host the tournament and geographic suitability. The competition would run for two weeks, and end with what had previously equaled District championship contests.
In the meantime, the annual swim championships were reduced to a one-day meet. Hosted at the University of Michigan, the meet would tax the endurance of individual swimmers, “since officials … decided to conduct semi-final events additional to the customary qualifying trials and finals.” That meant a swimmer entered in two events could compete six times during the day, with qualifying events in the morning, semifinals in the afternoon and finals swum at night. Perennial powers Battle Creek Central and Ann Arbor University High emerged as champions.
“The war to date has proved one thing conclusively – athletics in all schools must go on, for they serve to properly condition our young men for the bigger task ahead,” said MHSAA interim director Smith, speaking at an “annual football and basketball ‘bust’ for Lakeview High School” in Battle Creek in February 1943. Smith had served as principal at the high school for 14 years before taking over at the MHSAA. He “expressed regret” that the MHSAA had altered the various formats of the annual championships. According to coverage of the gathering in the Battle Creek Enquirer, “he intimated that it, along with all other forms of statewide competition, would be restored before another school year begins.”
Continued Chaos
The cities of Lansing and Kalamazoo played host to the most contingents, with 25 teams across the four enrollment classifications playing games at recently completed Lansing Sexton – the rechristened Lansing Central High School – and the Lansing Boys Vocational School. A total of 23 schools squared off at Western Michigan College of Education (now Western Michigan University).
As previously stated, transportation considerations meant some schools played above or below their normal classification to make things work. Ecorse, normally a Class B school, battled in the Class A tournament hosted at Dearborn Fordson. Benton Harbor, with Class A enrollment numbers, competed in the Class B tournament played across the St. Joseph River at St. Joseph High School instead of at the Kalamazoo Area tournament against similarly-sized schools.
A total of 128 area titles were awarded across the state’s two peninsulas. Decatur, the Class C state champion in 1942 with a 25-0 record, was the only team titlist to repeat in 1943, emerging with one of the “Area” crowns and extending its streak of victories to 41 consecutive. Also among the winners was Grand Rapids Union, a “cellar team in the regular season.”
“Although Union stood seventh in the city tally, the Red Hawks won the Area Tournament Crown in three smashing, spine-tingling battles,” stated the sports editor in the 1943 Aurora - Union’s yearbook. “In fast games the Hawks overcame Catholic and beat the Creston Bears … as well as whipping Davis Tech for their final victory.”
In April, the MHSAA confirmed that competition would end with area, city or conference meets in track, and again in tennis and golf, because of transportation, participation issues, and the “prospects of closing of some of the schools early.”
Various fans and media members grumbled about the unsatisfying conclusion to the prep sports calendars.
Hope
The coaching ranks were heavily hit by the war, as numerous mentors were tapped by the armed forces to lead physical fitness programs. Despite initial concerns, few “of the state’s 400 football-playing prep schools” dropped the sport come the 1943-44 school year. As it would turn out, because of the travel constraints, attendance increased as more and more sports fans turned to high school competition for entertainment.
Smith stated in October that he had “yet to find anyone who is definitely against bringing the (basketball) championship tournament back to life. There seems to be overwhelming sentiment in favor of the revival. The schools right-about face on the state cage classic which annually drew 700 prep teams and 11,000 players is explained by the fact coaches now feel the federal government is strongly in favor of any attempt to encourage or extend athletics. Last year schoolmen were not certain what the government’s attitude on sports would be and were hesitant about continuing athletics in pre-war style.”
 Only 258 of 614 schools replied to a questionnaire about restoring the winter basketball state championships, but 73 percent of respondents were in favor of such, and in December, the Representative Council voted to resume the final rounds of the tournaments.
Only 258 of 614 schools replied to a questionnaire about restoring the winter basketball state championships, but 73 percent of respondents were in favor of such, and in December, the Representative Council voted to resume the final rounds of the tournaments.
Born October 1918 in St. Johns, Michigan at the peak of the “Spanish Flu” pandemic, Hal Schram was a 25-year-old sports reporter for the Lansing State Journal when he covered the restart.
“State championship basketball and track competition once more became a part of (the) Michigan high school athletic program when the Representative Council of the MHSAA voted to reinstate these two state-wide tournaments after a suspension of one year,” he wrote.
According to Schram, “It was believed that student working hours, transportation, scarcity of balls and general lack of interest” still necessitated cancellation of golf and tennis tournaments for the year. Conduction of a swimming championship was left “in the hands of a committee representing schools which sponsor the sport … subject to the approval of the representative committee.”
Plans were to return the final rounds of the basketball tournament to Jenison Field House on the campus of Michigan State, which had hosted those rounds from 1940-42. However, the facility was in use by Army trainees for a physical fitness program.
“We would like to have the finals staged here very much,” said MSC athletic director Ralph Young, “but our obligations to the army come first.”
“Despite the hitch, the executive committee opted to stay in Lansing, playing Class A and C semifinal contests at the Boys Vocational School fieldhouse, and Class B and D semi games at Sexton High School. Finals were held at the Vocational gym.
“Fifty-five hundred spectators jammed their way into every nook and cranny of the Boys Vocational school fieldhouse last night to see four high school teams (Saginaw Arthur Hill, Marshall, Lansing St. Mary, Benton Harbor St. John) win championships in the Lower Peninsula tournament finals. With all seats taken almost before the first game started, the big floor was completely encircled by people sitting and standing before the finish,” wrote State Journal sports editor George S. Alderton. “By 6 o’clock, when the Class D game started, all seats in the side bleachers had been filled and most of the end bleachers were gone. The last vacancy was occupied before the Class C game started at 7:15 o’clock and from that time on, those who came either stood or seized a seat left by some departing fan. In many instances two sat down when one departed. Corners of the court were seething masses of humanity …”
United Press International wire reports indicated that 8,500 in total saw the Finals, as fans shifted in and out of the venue in support of the participating teams. “Some people had to be turned away at the finals,” said Smith, “and that certainly shows that people need and want this kind of relaxation.” The previous three Finals at MSC had drawn between 6,000-7,000 fans, while the 1939 Finals at I.M.A in Flint drew 5,000 and the 1938 event at Grand Rapids Civic Auditorium saw 6,000 attend.
“Lighting was so poor in the press box Friday night for the semi-finals,” added Alderton, “that workers came equipped with candles for the finals on Saturday night and propped them against their typewriters.”
Ishpeming hosted the Upper Peninsula Finals, as Escanaba, Crystal Falls, Channing and Amasa swept titles, respectively, in Classes B, C, D and Class E – the state’s smallest classification, reserved only for the smallest U.P. schools based on enrollment.
“Only complaint,” noted the Marquette Mining Journal, “was from those who couldn’t get in or were caught in a jam of fans seeking general admission seats. … Probably another 100 to 200 could have been accommodated if they were permitted to sit on the floor all along the court lines, but this would have been hazardous to players and fans …”
 (The Lower Peninsula finals returned to Jenison in 1945 – where they stayed, uninterrupted, through 1970 – and were played before 7,833 spectators that first season back. Locals were delighted as they watched Lansing Sexton top Benton Harbor’s undefeated Tigers, 31-30. Michigan Governor Harry Kelly “personally presented the Class B championship trophy to Sturgis Capt. Tom Tobar, congratulated Capt. Larry Thomson of East Lansing and then shook hands with the captains of the Class A contest before the game started.”)
(The Lower Peninsula finals returned to Jenison in 1945 – where they stayed, uninterrupted, through 1970 – and were played before 7,833 spectators that first season back. Locals were delighted as they watched Lansing Sexton top Benton Harbor’s undefeated Tigers, 31-30. Michigan Governor Harry Kelly “personally presented the Class B championship trophy to Sturgis Capt. Tom Tobar, congratulated Capt. Larry Thomson of East Lansing and then shook hands with the captains of the Class A contest before the game started.”)
In mid-May, “some 800 Michigan prep trackmen, survivors of 40 regionals at 10 centers” headed to Michigan State College to determine statewide champs. Only Kalamazoo in Class A and Birmingham in Class B held the chance to “repeat” as team champions. Instead, Saginaw Arthur Hill capped a stellar sports year, earning its first Class A team track title to go with its recently-earned basketball crown. (Earlier in the school year, the Lumberjacks also had opened their own football field.)
East Grand Rapids earned its second track title, grabbing the Class B crown. Fowlerville and Glen Arbor Leelanau brought home titles in Class C and D, respectively.
All sports – including golf and tennis which had gone three years without competing in a true state title round – returned to their original formats with the start of the 1944-45 school year.
In May 1945, Germany surrendered to the Allies, followed by Imperial Japan’s surrender, announced in August.
Participation in prep sports and attendance numbers would explode across the state and the nation in the coming years, tied to multiple factors, including, of course, the baby boom that followed World War II.

 Ron Pesch has taken an active role in researching the history of MHSAA events since 1985 and began writing for MHSAA Finals programs in 1986, adding additional features and "flashbacks" in 1992. He inherited the title of MHSAA historian from the late Dick Kishpaugh following the 1993-94 school year, and resides in Muskegon. Contact him at [email protected] with ideas for historical articles.
Ron Pesch has taken an active role in researching the history of MHSAA events since 1985 and began writing for MHSAA Finals programs in 1986, adding additional features and "flashbacks" in 1992. He inherited the title of MHSAA historian from the late Dick Kishpaugh following the 1993-94 school year, and resides in Muskegon. Contact him at [email protected] with ideas for historical articles.
PHOTOS: (Top) Grand Rapids Union was among "Area" boys basketball champions in 1943. (2) Lewis Forsythe, left, and Charles Forsythe were among leaders during the MHSAA's first decades (3) The Saginaw Arthur Hill yearbook for 1944 tells of fitness training undertaken by students. (4) Julian W. Smith served as interim MHSAA executive director while Charles Forsythe was serving in the military. (5) Flint Northern's Bill Hamilton earned all-state honors in 1942. (6) Western Michigan College was among hosts of 1943 Area tournaments. (7) Arthur Hill's yearbook celebrates the 1943-44 boys basketball championship. (8) Basketball Finals returned to Jenison Field House in 1945. (9) The MHSAA paid tribute to World War II veterans in its 1945 Basketball Finals program.

