
Turnaround Coaches: Study their Steps
April 27, 2016
 By Scott Westfall
By Scott Westfall
MSU Institute for the Study of Youth Sports
Turnaround leadership is often a popular topic within sports conversations, as many coaches are revered for their ability to transform a struggling team into a “winner.”
Turnarounds often are discussed in platitudes such as, “That coach has what it takes to turn this program around.”
While often talked about during the offseason, especially in the face of coaching vacancies, turnarounds are difficult to achieve. After all, if transforming a failing team into a successful one were an easy task, there would not be such an abundance of teams that struggle year-in and year-out.
As much as turnaround coaches are celebrated for their abilities to turn a losing program into a winner, very little scientific research has been devoted to analyzing coaches who have proven themselves as turnaround specialists. The steps and intangibles necessary for achieving a coaching turnaround have remained undetermined as this topic had never been examined from a scientific perspective – until now.
For the past year and a half, I have devoted the majority of my time to researching turnaround leadership in high school coaching, undertaking this study as the topic of my doctoral dissertation project. Research participants in this study included 11 high school football coaches from the state of Michigan who led dramatic turnarounds at their high schools within the last decade. The criteria for participant selection were:
• Prior to the coach’s arrival or appointment as head coach, the team finished (at least) three of the previous four seasons with a losing record (below .500 winning percentage), including a losing season immediately before the coach’s arrival or appointment.
• Within five seasons of the coach’s arrival, the team enjoyed (at least) three winning seasons (above .500 winning percentage).
Before their turnarounds occurred, these high schools had not experienced a winning season (on average) in 7.2 years, while five of the 11 schools had never qualified for the MHSAA Playoffs. However, upon being hired, the average time it took the coaches to achieve a winning record was 1.73 seasons. Moreover, the average time it took the coaches to qualify for the MHSAA Playoffs was 1.82 years. On top of this, each of the 11 teams qualified for the playoffs within three years of hiring their new coach.
The circumstances these coaches faced when they arrived were challenging to say the least, as all of the coaches entered a negative situation with poor team culture. These situations were characterized by losing streaks, cancelled seasons, dilapidated facilities, poor role models on the previous coaching staffs and a significant amount of parental pushback. Players and community members often were embarrassed by their football program. One coach described the situation by recounting, “During that time they were a doormat; everybody’s homecoming, a laughing stock. They were like the Bad News Bears.” Additional problems included low numbers, very little player development, and a low amount of commitment to the overall program.
One coach that I interviewed compared entering a turnaround situation to building a well. He stated, “You may not have success on the surface initially, but if you dig nice and deep and build the well right, there is water down there. It’s going to be some work and it might not come up right away – it takes some pumping. But if you build it right, it will happen.” In this article I will attempt to encapsulate 16 months of research, 191 pages of interview transcriptions, 2,278 miles driven across the state of Michigan, and countless hours spent with 11 turnaround coaches, in order to present to you the nucleus of what it takes to turn around a failing high school program.
The coaching philosophies of the majority of the coaches were characterized as “educational athletics.” This involved coaches striving to do things the right way, viewing their job as an extension of the classroom, implementing a character development program, and using football as a vehicle to teach life skills to players. Furthermore, their greatest strengths were revealed to be coaching/leadership skills, along with the ability to develop strong relationships with their players.
Coaches unanimously agreed that upon their arrival immediate changes needed to be made to the team’s culture. These changes included prioritizing team workouts, altering visible elements like the organization of practices, offensive and defensive schematics, team logos, along with placing positive role models in front of the players. Other changes to team culture happened through improved coach-athlete relationships, giving players a better football experience, and purging the program of negative people. One coach used the term, “Weeding the roses,” which means getting rid of the negative people in the program in order to let the better parts grow and prosper.
All of the coaches developed some type of vision for their program. The most common visions involved transforming their team into a top-level program, and for their players to conduct themselves as quality human beings. Winning games, competing with the best teams in their division, and playing for MHSAA championships marked becoming a top program. While winning was a major component of the coaches’ visions, developing quality human beings was revealed to be just as essential. This was evident as several coaches remarked that their most well-behaved kids were also their most productive players, and that doing things right in school and in the community often equates to wins on the football field.
To build upon their visions, each of the coaches formulated some type of plan or “blueprint” to execute their turnarounds. The majority of the coaches’ plans were constructed around developing positive coach-athlete relationships and employing off-season strength and conditioning programs. While all of the coaches’ plans eventually yielded a great amount of success, not all parties bought into them initially. Some of the players needed to see proof that the team could win games before they were completely sold. In order to create buy-in, the coaches used various approaches to connect with players and sell their plan. These methods included team activities, cultivating relationships with players, continuously selling their vision, hiring/retaining quality assistant coaches, and entering the situation with some sort of previous expertise. Although it may take time, the coaches stressed the importance of the players buying into their vision. As one of them decreed to his team, “The quicker you buy in, the quicker we win.”
Early indicators that a turnaround was commencing included winning games or making significant strides off of the field through positive coach-athlete relationships. Sources of sustained changes included a win streak or an increased level of commitment from the players. Clear indicators that the program had undergone a turnaround included the players adopting a new mentality filled with trust and confidence, along with the program reaching unprecedented levels of success, such as competing with the best teams, completing an undefeated season, and/or making the playoffs consistently.
Character development emerged as a strong component of this study, as 100 percent of the coaches reported that it played a significant role in fostering turnarounds. The coaches also indicated that they deliberately teach character in practice and use coaching as a platform for character development.
In hindsight, an outside observer may assume that these coaches were destined to succeed and their plans were met with little resistance. However, after examining their roads to turnaround success, most of them met several barriers along the way. Early obstacles included widespread mental challenges among players such as a lack of confidence and/or trust. Other early barriers included parental pushback and some cases of overt interference. After the turnarounds were complete, the coaches’ problems did not disappear; they simply changed form, as complacency became the new problem on the team. A potential root of this complacency was the addition of younger players who thought that success would happen automatically simply because of the program’s prior achievements.
The coaches were quick to acknowledge that the turnarounds would not have been possible without the excellent support they received. Their greatest source of help came from their assistant coaches who contributed both tangible and psychosocial support. Tangible support was seen through the assistants performing administrative duties and overseeing strength and conditioning sessions. Meanwhile, psychosocial support came in simple ways, such as listening, giving advice, and showing belief in the head coach. As one coach stated, “You’re only as good as the people you have around you.”
Team turnarounds are not officially complete until a team maintains the success it has built. In order to avoid complacency and sustain momentum, the coaches recommended that coaches and players find ways to keep reaching higher. In order to do this, coaches recommended talking to players about their team goals and what they want their legacies to be. To help sustain momentum, coaches stressed that it is often the little things that matter the most, such as effort, team discipline, player accountability, and positive attitudes.
The strongest theme that emerged from this study was the importance of coach-athlete relationships. All of the coaches believed that relationships are imperative to fostering turnarounds. It was also emphasized that relationships are crucial for sustaining long-term success. In essence, coaches may experience some momentary success by taking shortcuts with superior talent, however, strong relationships are the “X-factor” that will sustain the program over the long run. While the approaches of building relationships were diverse, what mattered most was coaches spending time with players in both structured and unstructured team activities, and simply showing players that they cared about them as people as much as they did as football players.
Steps of a Turnaround
(When turnarounds happen, they usually happen in this order)
1. Establish new leadership
2. Assemble a staff of positive role models
3. Gather information about the program
4. Create the vision
5. Make a plan and communicate it
6. Create buy-in from players and other key people
7. Change behavior – This is the impetus of the turnaround
8. Create and celebrate early wins
9. Don’t let up – Keep setting new goals and reaching higher
10. Complacency is the enemy: Make sure change sticks!
Intangibles Checklist
(These are the little things that people cannot see or do not talk about, yet they often matter the most)
1. Positive relationships between coaches and players. Build these by spending time with players and showing them you care about them as a person.
2. Establishment of a strength and conditioning program. All successful turnarounds were led by coaches who implemented a respectable offseason training program.
3. Display an undeniable belief that your vision and the plan will produce successful results. Continuously sell your plan and give players the reasons behind why you do what you do. Be prepared to stand tall and adhere to your vision when adversity strikes.
4. Generate player buy-in through team activities. Remember that sports are supposed to be FUN. Plan structured and non-structured activities to generate fun, excitement and team cohesion!
5. Demand excellence of your players off the field. Promote educational athletics and use your platform as a coach to teach character and life lessons to your players.
6. Outwork your opponents in everything you do. Arrive earlier. Stay later. Go above and beyond what your competitors are doing. Set the tempo that hard work is the new norm and it starts with you.
7. Remember that the little things matter. Take the time to ensure that your team always has the right effort, attitude and discipline, as well as accountability to the program and each other.
Scott Westfall spent 10 years as a teacher, coach, and athletic director in Fort Collins, Colo. He is currently finishing his Doctorate at Michigan State University, with an emphasis in Sport Psychology and Athletic Administration, and assisting the MHSAA with its student leadership programs. Westfall is a former athlete who participated in football, wrestling, tennis and cross country at the high school level, and rugby at the collegiate level. Please feel free to contact Scott if you would like a copy of his full dissertation. Scott also performs speaking engagements at conferences on various topics within educational athletics. He can be reached at [email protected]
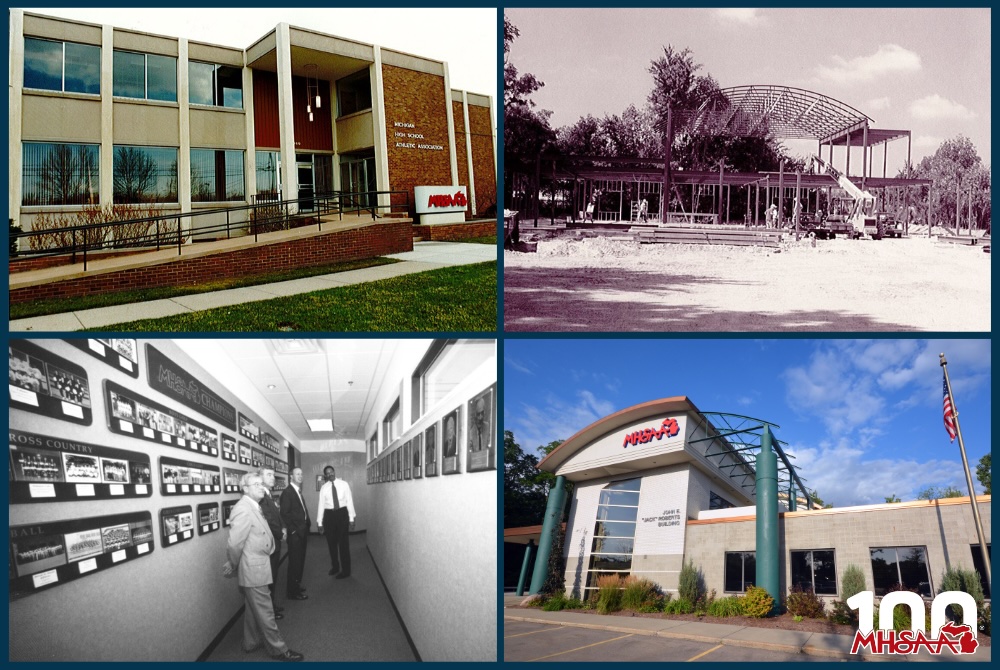

Century of School Sports: MHSAA's Home Sweet Home
By
Rob Kaminski
MHSAA benchmarks editor
November 5, 2024
Visitors to 1661 Ramblewood Drive for the multitude of MHSAA committee meetings, in-services and other functions are sure to see the faces of Michigan’s renowned educational athletics leaders throughout the years on various recognition boards.
Absent from any of those displays is the late East Lansing resident Thomas Reck. Yet, Reck and the long-range vision of Jack Roberts were equally as vital in “restructuring” the MHSAA in the late 1990s; quite physically.
“I really wanted something along US-127 – visible from 127 – and there was a good deal of open land where the building sits now that looked to be about the right size,” recalled Roberts, who at the time was just finishing the first decade of what would be an iconic 32-year run as the executive director of the MHSAA.
There was one potential roadblock to Roberts’ dream location: There was no indication of any kind that the property was for sale; no billboard, no realty listing.
That’s because it wasn’t for sale – yet.
“I contacted a realtor, Martin Property Development, and I suggested one of their employees call upon Mr. Reck,” Roberts said. “He did that, and got a purchase price of $600,000. To me, the excitement really took place before the first shovel went into the ground.”
The deal was then approved by both parties, and development began in 1996, with Reck’s residence remaining in place atop the small hill south of the new road leading to the proposed site of the MHSAA building.
“When we bought the land, there was no road,” Roberts said. “One of the reasons it curves is that Mr. Reck was given a life lease, so we had to go around his house. It also had to navigate some protected wetland areas.”
As for the name of the road, that was the MHSAA’s choice, one which actually came quite easily. The city of East Lansing had some concerns with the new development, and expanding on an existing name for the road was the first show of good faith by the newest tenants. Keeping the name Ramblewood made sense as there was already a Ramblewood Drive at the exact intersection to the east of Coolidge Road.
“We didn’t want to come in and change a lot of things, or inconvenience the residents in that area,” Roberts said. “We kept development back from the road and kept as much nature intact as possible. Even the signs that are there now are off the road and relatively small.”
Roberts and staff needed no signs to find their way to the new digs just more than three miles north of the previous offices on Trowbridge Road.
 Led by Roberts and former assistant director Tom Minter, much of the moving occurred during Christmas break of 1996. Doors to the new building were opened in January 1997, roughly seven years after Roberts first began dreaming of a new home.
Led by Roberts and former assistant director Tom Minter, much of the moving occurred during Christmas break of 1996. Doors to the new building were opened in January 1997, roughly seven years after Roberts first began dreaming of a new home.
The building on Trowbridge was formerly a credit union, and its structure provided some unique problems.
“In the late 1980s, around ‘88 or ‘89, we bought our first major computer, an IBM mainframe, and put it upstairs in the old building,” Roberts said. “It was about five feet high and eight feet wide and had its own room. We had to drill through concrete to wire it. I began to realize that we were going to have a hard time keeping up with things in a building that was so difficult to modernize.”
John Johnson, the MHSAA’s first communications director and a pioneer in that position among state high school associations, also reflected on the early days.
“Anything which was data-driven was jobbed out for awhile,” Johnson said. “Football playoff rankings were delivered to us once a week from a third party. We were doing everything outside the building: school databases, officials databases, penalty databases. The only thing we had inside the walls was word processing. I had the first PC in 1987.”
And, he recalled, the beast of a mainframe that took up an entire room at the expense of personnel. “Yep, it took up the whole room,” Johnson confirmed. “I was in what was called the library, which had historical books, but also old T-shirts left over from previous years’ champions.”
That lack of storage was also motivation for Roberts to find new real estate, and addressing that shortcoming was paramount in the plans.
“We had no storage, and no efficient way to receive shipments like rules books, paper, and the basic supplies we needed to run our business,” Roberts said. “That’s also why we have the lift in its current location at the new building; shipping and receiving were really important to us, along with our drop ceiling which made it much easier to run wiring as needed.”
As sparkling and expansive as the new facilities were, perhaps the best feature of all was its cost. The structure only took up a portion of the land purchased by the association, per Roberts’ vision. That left four parcels on the property for sale by the MHSAA, and with the road and utilities in place, those sections became even more valuable and enticing.
The MHSAA’s expenditures totaled roughly $1 million for the purchase of the land, road construction and utility installations. The parcels then sold for approximately $300,000 apiece.
“In the end, we had our space free of charge, and had $200,000 for furnishings,” Roberts said. The lone cost would then be the actual construction of the building, financed through a bond. And, the MHSAA could choose their neighbors, which was also part of the grand plan.
“We were going to be particular about who moved in, and that they’d be further back; not right on the road,” Roberts said. “Above all, we wanted to be good neighbors to the residents in the area and choose businesses that would be good neighbors as well.”
The other four parcels are occupied by medical practices, and the area remains a somewhat sleepy and hidden subdivision to this day.
Interestingly, and unknown to most, the MHSAA nearly held on to the parcel closest to its front door as a rental venture. That prospect led to spirited but friendly debate among Representative Council members at the time, leading to a vote on the matter of whether to sell the land or construct another building and rent space in that structure.
“There was good-natured discussion on the topic with arguments both in favor of selling and for building and renting on that last parcel,” Roberts said. “I remember on the morning of the vote, I offered the Council this to think about: We were really good at rules, really good at interpretations and administration of school sports. None of us were landlords or experts in that field.”
By a 10-9 vote, the Association would sell the final plot. “We didn’t get greedy, and history showed it was the right decision, what with the housing market landscape years later,” Roberts said. “We’d already won the lottery in a sense. Why enter into an area in which we knew little about?”
The timing of this new gem couldn’t have been any better, as the MHSAA was hosting the Section 4 meeting of state high school associations in September 1997. It was the perfect opportunity to showcase the facility with an open house attended by those in town for the meeting as well as current and former MHSAA staff and dignitaries.
Met with the now-recognizable and unique high-arching “roof” – half copper and half green, open frame – visitors were impressed. “The architect was on vacation in Florida and saw a similar building with the copper roof. When she assured me that it wouldn’t turn green over time, I agreed to do it,” Roberts said. “The design is actually still trendy, so it’s held up over time.”
Indeed it has, as verified by builders and designers currently giving the MHSAA’s home its first facelift.
“When I told people how old the building was, they couldn’t believe it, because its design has held up so well,” said MHSAA Assistant Director Dan Hutcheson, who has worked closely with contractors on building renovations during the last several months.
Even prior to this expansion and cosmetic overhaul, the MHSAA and its technology, staff were looking to the future.
 “Ironically, we upgraded projectors and cameras to delve into Zoom and virtual meetings before we really even knew what they were or how valuable they could be,” Hutcheson said. “This was winter of 2020, and a couple months later, Covid hits and by luck we’re kind of prepared, at least communication-wise.”
“Ironically, we upgraded projectors and cameras to delve into Zoom and virtual meetings before we really even knew what they were or how valuable they could be,” Hutcheson said. “This was winter of 2020, and a couple months later, Covid hits and by luck we’re kind of prepared, at least communication-wise.”
Following the Covid-19 pandemic, once the MHSAA was back on solid footing, Executive Director Mark Uyl began to outline and identify areas for expansion and updating inside the building.
Roberts’ foresight in the initial storage and expansion areas have paid huge dividends, as plenty of space existed for new offices.
The first meeting with architects post-pandemic was in September 2022, with renovations beginning in September 2023. Now, two years later, the project is near completion.
New color schemes, video boards, LCD displays and touchscreens serve to keep the facility in stride with those to which the MHSAA’s constituents have become accustomed.
There was plenty of work behind the scenes, too, such as fixtures and plumbing which simply had exceeded their lifespan or needed to be brought up to current codes. The overall mission for the changes, as always, was to better serve the membership.
“We serve 750 member schools, with so many from those schools coming here for training, teaching and educational sessions,” Hutcheson said. “As our staff members visit schools around the state, we see video boards, electronic message boards. We needed to keep in step with the schools, and in doing so, better assist our ADs, coaches and officials with their work.”
For two people who didn’t know one another, Reck and Roberts brought countless people together since 1997 to help them do their work.
Previous "Century of School Sports" Spotlights
Oct. 29: MHSAA Summits Draw Thousands to Promote Sportsmanship - Read
Oct. 23: Cross Country Finals Among MHSAA's Longest Running - Read
Oct. 15: State's Storytellers Share Fall Memories - Read
Oct. 8: Guided by 4 S's of Educational Athletics - Read
Sept. 25: Michigan Sends 10 to National Hall of Fame - Read
Sept. 25: MHSAA Record Books Filled with 1000s of Achievements - Read
Sept. 18: Why Does the MHSAA Have These Rules? - Read
Sept. 10: Special Medals, Patches to Commemorate Special Year - Read
Sept. 4: Fall to Finish with 50th Football Championships - Read
Aug. 28: Let the Celebration Begin - Read
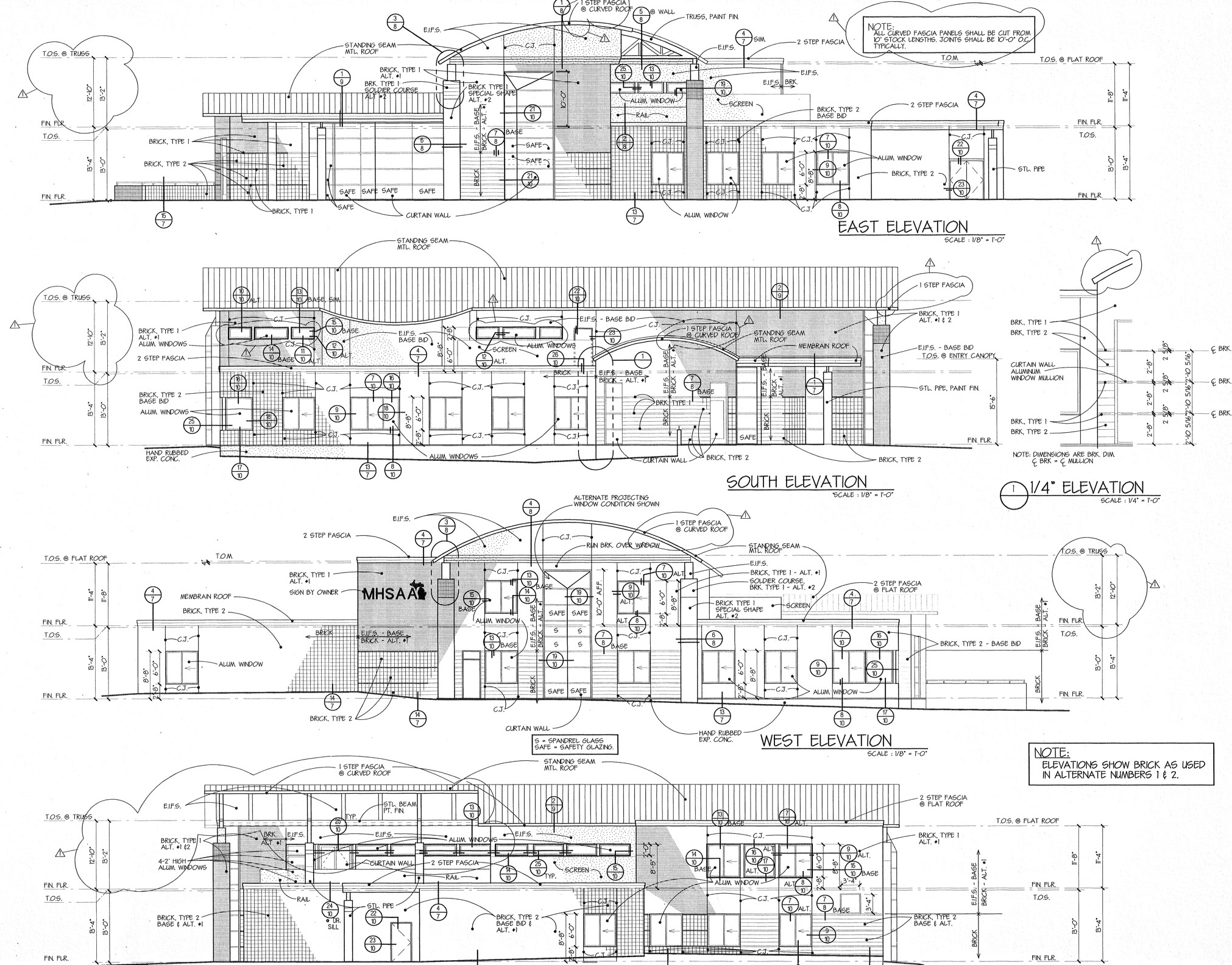
PHOTOS (Top) Clockwise from top left: The former MHSAA office on Trowbridge Road. (2) Work is underway on the new MHSAA building on Ramblewood Drive. (3) The MHSAA office on Ramblewood before recent updates that included a switch from green to gray on the exterior. (4) Now-retired assistant director Nate Hampton, far right, and others walk the upstairs hallway of the recently-built Ramblewood building. (Middle) Blueprints for the Ramblewood office exterior. (Below) Past Executive Director Al Bush (right) and his wife, Lois, were on hand for the 1997 open house hosted by then-Executive Director Jack Roberts (left) and staff. (MHSAA file photos.)

